13-22
MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual
MOTOROLA
Part IV. Hardware Interface
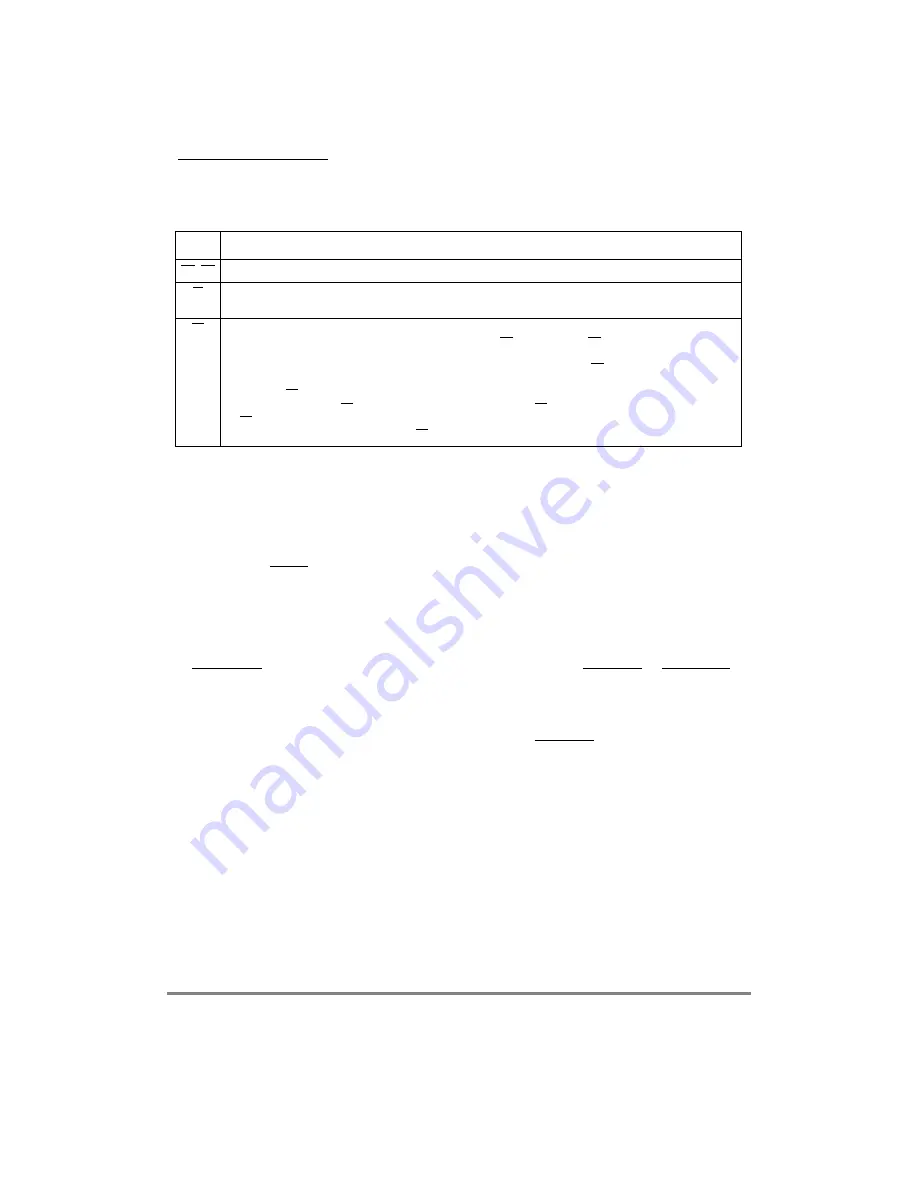
Table 13-2 summarizes when active pull-up drivers are enabled as outputs.
The purpose of active pull-up buffers is to allow access to zero wait-state logic that drives
a shared signal on the clock cycle immediately following a cycle in which the signal is
driven by the MPC860. In other words, it eliminates the need for a bus turn-around cycle.
13.3 Internal Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors
The TMS and TRST pins have internal pull-up resistors. MPC860 devices from Rev 0 to
Rev A.3 (masks xE64C and xF84C) have an internal pull-up resistor on TCK/DSCK but no
internal pull-up resistor on TDI/DSDI. This was corrected on Rev B and later; on these
chips, the internal pull-up resistor was removed from TCK/DSCK and an internal pull-up
resistor was added to TDI/DSDI.
If RSTCONF is pulled down, during hardware reset (initiated by HRESET or PORESET),
the data bus D[0Ð31] is pulled down with internal pull-down resistors. These internal
pull-down resistors are to provide a logic-zero default for these pins when programming the
hard reset conÞguration word (See Section 12.3.1.1, ÒHard Reset ConÞguration Word.Ó).
These internal pull-down resistors are disconnected after HRESET is negated.
No other pins have internal pull-ups or pull-downs.
Resistance values for internal pull-up and pull-down resistors are not speciÞed because
their values may vary due to process variations and shrinks in die size, and they are not
tested. Typical values are on the order of 5 K
W
but can vary by approximately a factor of 2.
13.4 Recommended Basic Pin Connections
The following sections provided recommended pin connections.
Table 13-2. Active Pull-Up Resistors Enabled as Outputs
Signal
Description
TS, BB When the MPC860 is the external bus master throughout the entire bus cycle.
BI
When the MPC860Õs memory controller responds to the access on the external bus, throughout the entire
bus cycle.
TA
When the MPC860Õs memory controller responds to the access on the external bus, then:
¥ For chip selects controlled by a GPCM set for external TA, the MPC860Õs TA buffer is not enabled as an
output.
¥ For chip-selects controlled by the GPCM set to terminate in n wait-states, TA is enabled as an output on
cycle (n-1) and driven high, then is driven low on cycle n, terminating the bus transaction. External logic
can drive TA at any point before this, thus terminating the cycle early. [For example, assume the GPCM is
programmed to drive TA after 15 cycles. If external logic drives TA before 14 clocks have elapsed then the
TA is accepted by the MPC860 as a cycle termination.]
¥ For UPM-controlled chip selects, the TA buffer is enabled as an output throughout the entire bus cycle.
Summary of Contents for MPC860 PowerQUICC
Page 3: ...MPC860UM AD 07 98 REV 1 MPC860 PowerQUICC ª UserÕs Manual ...
Page 36: ...xxxvi MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA CONTENTS Paragraph Number Title Page Number ...
Page 78: ...I iv MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 88: ...1 10 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 114: ...3 16 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part I Overview ...
Page 226: ...8 32 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II PowerPC Microprocessor Module ...
Page 262: ...9 36 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part II PowerPC Microprocessor Module ...
Page 274: ...III iv MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III Configuration ...
Page 320: ...12 12 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part III Configuration ...
Page 325: ...MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface IV v Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 326: ...IV vi MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 352: ...13 26 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 394: ...14 42 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 426: ...15 32 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 530: ...17 26 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part IV Hardware Interface ...
Page 632: ...21 44 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 660: ...22 28 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 708: ...24 24 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 748: ...27 20 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 846: ...31 20 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 914: ...35 12 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 948: ...36 34 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part V The Communications Processor Module ...
Page 998: ...37 48 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Part VI Debug and Test ...
Page 1016: ...A 10 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1024: ...B 8 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1030: ...C 6 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA Appendixes ...
Page 1086: ...Glossary 12 MPC860 PowerQUICC UserÕs Manual MOTOROLA ...
Page 1106: ......
















































