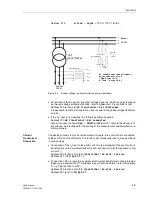
Functions
6-20
7SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C156-2
These values may either apply to the entire line length or be based on a per unit of line
length, as the quotients are independent of length. Furthermore it makes no difference
if the quotients are calculated with primary or secondary values.
For overhead lines it is generally possible to calculate with scalar quantities as the
angle of the zero sequence and positive sequence system only differ by an insignifi-
cant amount. With cables however, significant angle differences may exist as illustrat-
ed by the following example.
Calculation example:
110 kV single conductor oil-filled cable 3
×
185 mm
2
Cu with the following data
Z
1
/s = 0.408·e
j73°
Ω
/km
positive sequence impedance
Z
0
/s = 0.632·e
j18,4°
Ω
/km
zero sequence impedance
(where s = line length)
The calculation of the earth impedance (residual) matching factor K
0
results in:
The magnitude of K0 is therefore
When determining the angle, the quadrant of the result must be considered. The fol-
lowing table indicates the quadrant and range of the angle which is determined by the
signs of the calculated real and imaginary part of K
0
.
In this example the following result is obtained:
The magnitude and angle of the earth impedance (residual) matching factors setting
for the first zone Z1 and the remaining zones of the distance protection may be differ-
ent. This allows to set the exact values for the protected line, while at the same time
the setting for the back-up zones may be a close approximate even when the following
lines have substantially different earth impedance ratios (e.g. cable after an overhead
line). Accordingly, the settings for the address
1120
K0 (Z1)
and
1121
Angle
K0(Z1)
are determined with the data of the protected line while the addresses
1122
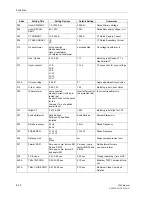
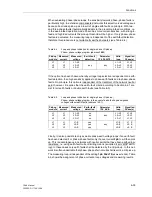
Table 6-1
Quadrants and range of the angle of K
0
Real part
Imaginary
part
tan
ϕ
(K0)
Quadrant/Range
Rules for calculation
+
+
+
I
0° ... +90°
arctan(|
Im
|/|
Re
|)
+
–
–
IV
–90° ... 0°
–arctan(|
Im
|/|
Re
|)
–
–
+
III
–90° ... –180°
arctan(|
Im
|/|
Re
|) – 180°
Z
0
Z
1
------
0.632
0.408
---------------
e
j(18.4°–73°)
⋅
1.55 e
⋅
–j54.6°
1.55
0.579
j0.815
–
(
)
⋅
=
=
=
=
0.898 – j1.263
K
0
1
3
---
Z
0
Z
1
------
1
–
è
ø
ç
÷
æ
ö
⋅
1
3
---
0.898
j1.263
–
1
–
(
)
⋅
1
3
---
0.102
–
j1.263
–
(
)
⋅
=
=
=
K
0
1
3
---
0.102
–
2
(
)
1.263
–
2
(
)
+
⋅
0.42
=
=
ϕ
K
0
(
)
arc tan
1.263
0.102
---------------
è
ø
æ
ö
180°
–
94.6°
–
=
=
Содержание siprotec 7SA6
Страница 2: ...Siemens Aktiengesellschaft Book No C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 18: ...xviii 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 32: ...Introduction 1 14 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 82: ...Hardware and Connections 2 50 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 119: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Страница 190: ...Configuration 5 62 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 559: ...Control During Operation 7 45 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 7 45 Circuit breaker trip test in DIGSI 4 ...
Страница 652: ...Installation and Commissioning 8 78 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 724: ...Technical Data 10 56 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 ...
Страница 800: ...Appendix A 76 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 866: ...Appendix B 66 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...