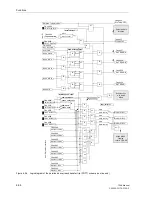
Functions
6-102
7SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C156-2
6.6.1.6
Unblocking with Z1B
The following scheme is suited for conventional transmission media.
Principle
The unblocking method uses a permissive release principle. It differs from the permis-
sive overreach transfer scheme (Sub-section 6.6.1.4) in that tripping is possible also
when no release signal is received from the opposite line end. It is accordingly mainly
used on long lines, if the signal is transmitted via the protected line with power line car-
rier (PLC), and the attenuation of the transmitted signals at the fault location can be
so severe that the reception at the other line end cannot be guaranteed in all cases.
Here, a special unblocking logic takes effect.
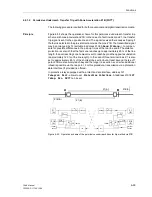
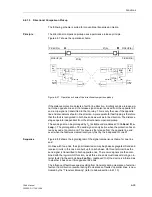
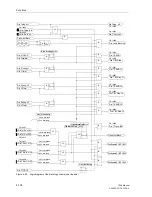
Figure 6-59 shows the operation scheme.
Two signal frequencies which are keyed by the transmit output of the 7SA6 are re-
quired for the transmission. If the transmission device has a channel monitoring, then
the monitoring frequency f
0
is keyed over to the working frequency f
U
(unblocking fre-
quency) f
U
. When the protection recognizes a fault inside the overreaching zone Z1B,
it initiates the transmission of the unblock frequency f
U
. During the quiescent state or
during a fault outside Z1B, or in the reverse direction, the monitoring frequency f
0
is
transmitted.
If the unblock frequency f
U
is faultlessly received from the opposite end, a release sig-
nal is routed to the trip logic. Accordingly, it is a prerequisite for fast tripping, that the
fault is recognized inside Z1B in the forward direction at both line ends. The distance
protection is set such that the overreaching zone Z1B reaches beyond the opposite
station (approximately 120 % of line length). On three terminal lines Z1B must be set
to definitely reach beyond the longer line section even when intermediate infeed via
the tee point is present. The first zone is set in accordance with the usual grading
scheme, i.e. approximately 80 % of the line length; on three terminal lines at least be-
yond the tee point.
The transmit signal can be prolonged by T
S
(settable under address
2103A
Send
Prolong.
). The extension of the transmit signal is only effective when the protection
has already issued a trip command. This ensures release of the opposite line end even
when the short circuit has been switched off rapidly by the independent zone Z1.
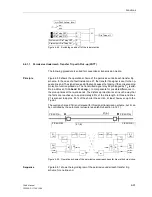
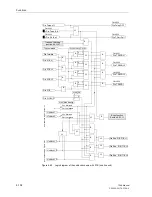
Figure 6-59
Operation scheme of the unblocking method with Z1B
A
B
Z1(A)
Z1(B)
Z1B(A)
Z1B(B)
Z1B
T1B
T
S
&
≥
1
trip
transm.
rec.
further
zones
&
Z1 or
≥
1
T
S
&
≥
1
trip
transm.
rec.
further
zones
&
Z1 or
≥
1
f
U
f
U
f
0
f
0
Unblock-
logic
Unblock-
logic
U
U
B
B
f
0
–
Off frequency (monitoring frequency)
f
U
–
Unblock frequency (send frequency)
U –
Unblocking signal
B –
Blocking signal
(A)
Z1B
T1B
(B)
Содержание siprotec 7SA6
Страница 2: ...Siemens Aktiengesellschaft Book No C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 18: ...xviii 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 32: ...Introduction 1 14 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 82: ...Hardware and Connections 2 50 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 119: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Страница 190: ...Configuration 5 62 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 559: ...Control During Operation 7 45 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 7 45 Circuit breaker trip test in DIGSI 4 ...
Страница 652: ...Installation and Commissioning 8 78 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 724: ...Technical Data 10 56 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 ...
Страница 800: ...Appendix A 76 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 866: ...Appendix B 66 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...