Functions
6-89
7SA6 Manual
C53000-G1176-C156-2
6.6
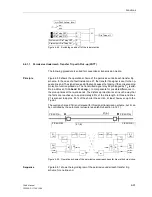
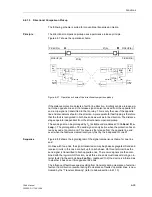
Teleprotection Schemes with Distance Protection
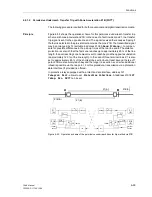
Purpose of Telepro-
tection
Short-circuits which occur on the protected line, beyond the first distance zone, can
only be cleared selectively by the distance protection after a delay time. On line sec-
tions that are shorter than the smallest sensible distance setting, short-circuits can
also not be selectively cleared instantaneously.
To achieve non-delayed and selective tripping on 100 % of the line length for all faults
by the Distance Protection, the Distance Protection can exchange and process
information with the opposite line end by means of signal transmission systems. For
this purpose, the device has signal send outputs and receive inputs as well as
associated logic functions. This can be done in a conventional way using send and
receive contacts. As an alternative, digital communication lines can be used for signal
transmission (ordering option).
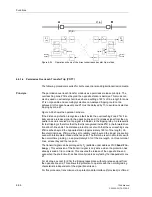
Teleprotection
Schemes
A distinction is made between underreach and overreach schemes.
The Distance Protection is set with normal zone grading characteristic. An additional
fast overreaching zone Z1B is available for teleprotection schemes. Signal transmis-
sion and trip release methods depend on the teleprotection scheme. At least one re-
verse looking distance zone may be required for some teleprotection schemes. It is
recommended to use zone Z3 for this purpose.
The 7SA6 permits:
•
PUTT (Pickup)
•
Permissive Underreach Transfer Trip with Zone Acceleration Z1B (PUTT)
•
Direct Transfer Trip without Pickup
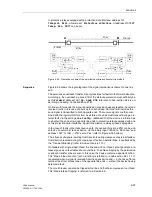
In the comparison scheme of the Distance Protection an accelerated overreach zone
applies from the outset. It can only trip if a fault is also recognized at the other line end
in an overreach zone. A release signal or a blocking signal is transmitted. The follow-
ing are available:
Release scheme:
•
Permissive Overreach Transfer Trip (POTT)
•
Directional Comparison Pickup
•
Unblocking with Overreach Zone Z1B
Blocking scheme:
•
Blocking with Overreach Zone Z1B
Schemes via pilot wire:
•
Pilot Wire Comparison
•
Reverse Interlocking
As the distance zones Z1 ... Z5 (without Z1B) function independently, instantaneous
tripping in Z1 without a release signal is always possible. If instantaneous tripping in
Z1 is not required (e.g. in very short lines), then Z1 must be delayed with T1.
Содержание siprotec 7SA6
Страница 2: ...Siemens Aktiengesellschaft Book No C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 18: ...xviii 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 32: ...Introduction 1 14 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 82: ...Hardware and Connections 2 50 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 119: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Страница 190: ...Configuration 5 62 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 559: ...Control During Operation 7 45 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 Figure 7 45 Circuit breaker trip test in DIGSI 4 ...
Страница 652: ...Installation and Commissioning 8 78 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 724: ...Technical Data 10 56 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 ...
Страница 800: ...Appendix A 76 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...
Страница 866: ...Appendix B 66 7SA6 Manual C53000 G1176 C156 2 ...