2–28
Altera Corporation
Stratix II GX Device Handbook, Volume 2
October 2007
Transmitter Modules
Channel Clock Distribution
This section describes clocking within each channel for:
■
Individual channels in Basic (without ×4 clocking enabled),
SONET/SDH, PIPE x1, GIGE, (OIF) CEI PHY Interface (with
low-jitter option disabled), Serial RapidIO, SDI, and CPRI modes
■
Bonded channels in XAUI, PIPE ×4, PIPE ×8, Basic (with ×4 clocking
enabled), and (OIF) CEI PHY Interface (with low-jitter option
enabled) modes
Individual Channels Clocking
In individual channel modes, the transmitter logic is clocked by the
slow-speed clock from the clock divider block. The transmitter phase
compensation FIFO buffer and the PIPE interface (in PIPE mode) are
clocked by the
tx_clkout
clock of the channel that is fed back to the
transmitter channel from the PLD logic.
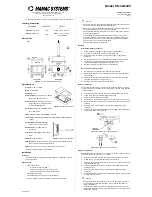
Figure 2–16
shows the clock
routing for the transmitter channel.
Figure 2–16. Individual Channel Transmitter Logic Clocking
The receiver logic clocking has two clocking methods: one when rate
matching is used and the other when rate matching is not used.
If rate matching is used (PIPE, GIGE, and Basic modes), the receiver logic
from the serializer to the rate matcher is clocked by the recovered clock
from its associated channel. The rest of the logic is clocked by the slow
clock from the clock divider block of its associated channel. The read side
of the phase compensation FIFO buffer and the PIPE interface (for PIPE
mode) is clocked by the
tx_clkout
fed back through the PLD logic.
Figure 2–17
shows the clocking of the receiver logic with the rate matcher.
Byte
Serializer
Transmitter Analog Circuits
Transmitter
Digital
Logic
Serializer
PLD
Logic
Array
Phase
Compen-
FIFO
sation
TX
8B/10B
Encoder
PIPE
Interface
XCVR
Central Block
Reference
Clocks
tx_clkout
÷
1, 2