5-27
TI 71M01D06-01EN 3rd Edition: 2012.12.01
5.12.3
Selecting Fuse
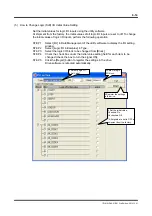
Verify that the inrush current is within the range
of the meltdown characteristics curve. Note,
however, that this characteristics curve is
created based on average data values.
Therefore, a certain margin must be taken into
account.
Moreover, since a fuse melts down due to joule
heat, the nominal rated value of
l
2
t
is specified
in the catalog. Check that the value of
l
2
t
due to
inrush current is less than the rated value. Since
the nominal rated value of
l
2
t
decreases in the
case of repetitive inrush current, if the number of
inrushes is 10,000 times, a margin factor of three
to four is required. Please confirm with the
manufacturer regarding the reduction in the
nominal rated value of
l
2
t
in the case of repetitive
inrush current.
The value for
l
2
t
is as follows in the case of
Section 5.12.1, "Inrush Current Waveforms."
Calculate l2t until the peak current of lp becomes
the rated current of the fuse or less, and then
add all the values.
Control power supply
2
2
3
3
2
3
2
2
2
2
2
1
)
(
2
t
I
t
I
t
I
t
I
P
P
P
CONT
×
+
×
+
×
=
24
.
0
2
10
2
2
2
10
4
3
3
10
3
5
.
15
3
2
3
2
3
2
=
×
×
+
×
×
+
×
×
=
−
−
−
Main power supply
31
.
3
2
10
7
14
2
10
7
5
.
19
2
10
6
8
.
20
3
2
3
2
3
2
=
×
×
+
×
×
+
×
×
=
−
−
−
2
2
2
3
2
3
2
2
2
2
2
1
)
(
2
t
I
t
I
t
I
t
I
P
P
P
MAIN
×
+
×
+
×
=
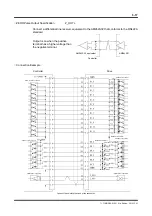
Example of meltdown characteristics curve
Current (A)
Meltdown time (s
econds)