2-24
TI71M01D06-01EN 3rd Edition: 2012.12.01
2.10.3 How to Calculate Regenerative Resistor Power Consumption
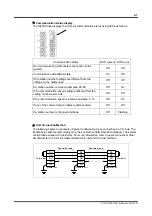
The calculation method of regeneration energy explained here assumes that the repeated
operation takes place at constant angular acceleration as shown in the figure below. If the
inertia is the same but the angular acceleration is small, there are cases where the current
conducted in the motor decreases and loss at motor and power AMP decreases accordingly,
thus increasing the current regenerated in the electrolyte capacitor. Thus, if there are several
angular acceleration patterns, the regeneration power consumption needs to be calculated for
each angular acceleration pattern.
t
dec
N
rmax
t
cy
t
const
t
acc
t
0
t
1
Mot
or v
elo
ci
ty
(rp
s)
(1) Consumption and processing of regeneration energy
Regeneration energy is consumed and processed in the drive as shown in the figure below.
Kinetic energy accumulated in the load inertia and rotor inertia is converted into current by the
motor and consumed by motor loss (coil copper loss) and power AMP loss. Excessive kinetic
energy is used to charge a smoothing capacitor. If the terminal voltage of the smoothing
capacitor reaches approximately 385 V, the regenerative resistor is activated to consume the
excess regeneration energy.
Motor loss
Power AMP loss
Smoothing
capacitor
Drive
Regeneration
resistor
Motor
+
load
Regeneration
current
(2) Changes due to motor output time
The output power at motor deceleration decreases
over time as shown in the graph to the right. On the
other hand, the motor copper loss and power AMP
loss always remain constant as the current becomes
mostly constant if the motor is decelerated at a
constant torque. For this reason, if the motor output is
greater than the loss power, excessive energy is
used to charge the smoothing capacitor. Current is
conducted in the regenerative resistor if this energy
(shaded area in the graph at right) exceeds the
allowable value.
P
OM
t
0
t
C
t
1
P
TL
Motor copper loss +
power AMP loss power
Motor output power
Time
Po
we
r