Writing Scripts with Lingo
437
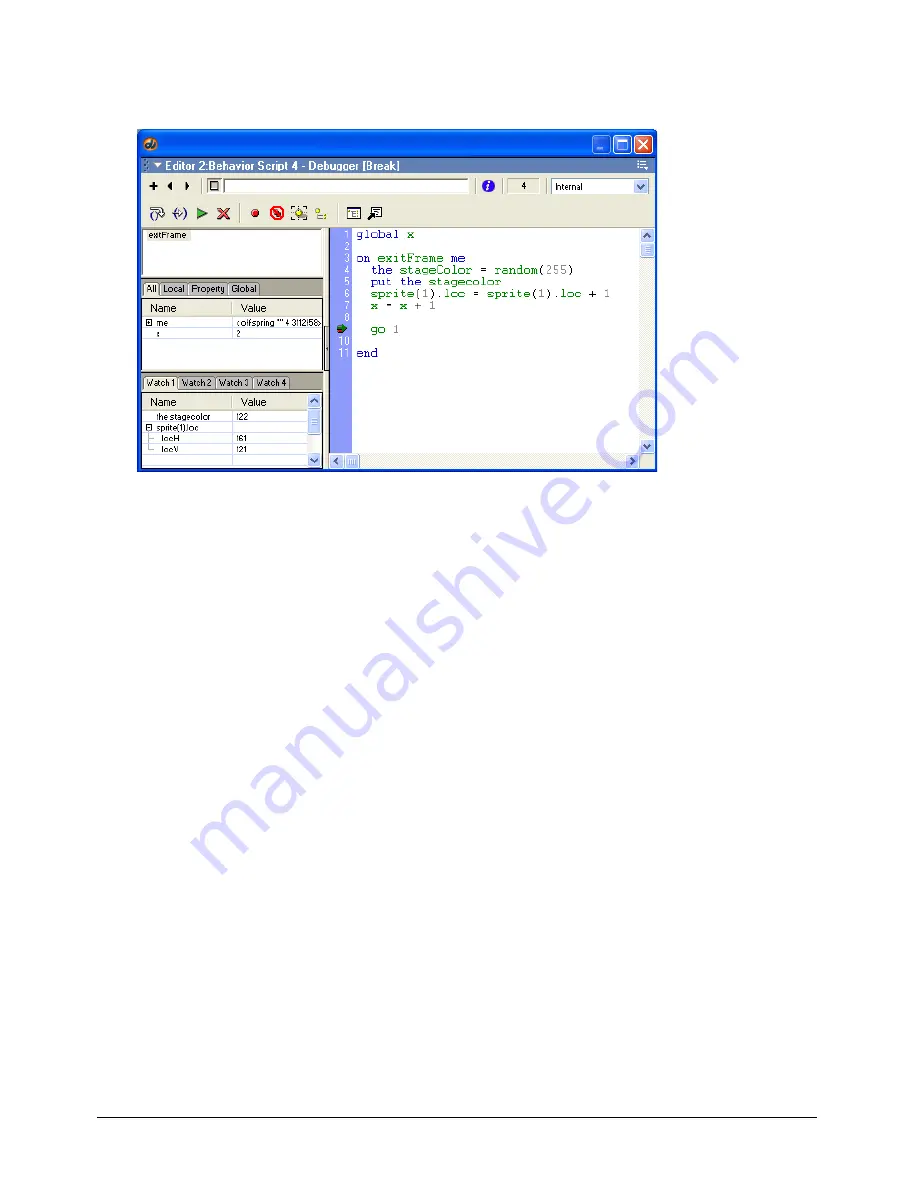
When the Debugger window opens, it shows the current line of Lingo and offers several choices
for what to run next.
To see which is the current line of Lingo:
•
Look for the green arrow next to a line of Lingo in the Script pane.
The green arrow points to the current line. You can’t select a different line of Lingo by clicking
it in the Script pane.
Viewing the call stack
The Call Stack pane, located in the upper left of the Debugger window in the preceding
illustration, displays the sequence of nested handlers that ran before the current line of code. This
sequence is called the call stack. Use the call stack to keep track of the structure of your Lingo
while you are debugging. You can view the variables associated with a specific handler by clicking
the handler name in the Call Stack pane. The variables are displayed in the Variable pane.
Viewing variables in the Variable pane
The Variable pane displays the variables associated with the current handler. The current handler
is the handler displayed in the Script pane and the last handler displayed in the Call Stack pane.
You can also display the variables associated with previous handlers in the call stack. As you step
through a script, changes to the values of any of the variables are displayed in red. For more
information about stepping through scripts, see “Stepping through scripts” on page 439.
Summary of Contents for DIRECTOR MX-USING DIRECTOR MX
Page 1: ...Using Director MX Macromedia Director MX...
Page 12: ...Contents 12...
Page 156: ...Chapter 4 156...
Page 202: ...Chapter 6 202...
Page 244: ...Chapter 7 244...
Page 292: ...Chapter 10 292...
Page 330: ...Chapter 12 330...
Page 356: ...Chapter 13 356...
Page 372: ...Chapter 14 372...
Page 442: ...Chapter 16 442...
Page 472: ...Chapter 18 472...
Page 520: ...Chapter 19 520...
Page 536: ...Chapter 20 536...
Page 562: ...Chapter 23 562...
Page 566: ...Chapter 24 566...
Page 602: ...Chapter 27 602...






























