X20 system modules • Analog input modules • X20AI2438
X20 system User's Manual 3.10
229
Transmitting and receiving
If a channel is synchronized, then the opposite station is ready to receive messages from the transmitter. Before
the transmitter can send data, it needs to first create a transmit array in order to meet FlatStream requirements.
The transmitting station must also generate a control byte for each segment created. This control byte contains
information about how the subsequent part of the data being transmitted should be processed. The position of the
next control byte in the data stream can vary. For this reason, it must be clearly defined at all times when a new
control byte is being transmitted. The first control byte is always in the first byte of the first sequence. All subsequent
positions are determined recursively.
FlatStream formula for calculating the position of the next control byte:
Position (of the next control byte) = Current po 1 + Segment length
Example:
Three autonomous messages (7 bytes, 2 bytes and 9 bytes) are being transmitted using an MTU with a width of
7 bytes. The rest of the configuration corresponds to the default settings.
Message 1:
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
B1
B2
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
No more data to transmit
-
-
...
-
Message 2:
Message 3:
Sequence for bus cyc. 1
Sequence for bus cyc. 2
Sequence for bus cyc. 3
Sequence for bus cyc. 4
Sequence for bus cyc. 5
Sequence for bus cyc. 6
B1
B2
A2
A3
A4
C2
A1
A7
A5
A6
C3
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
-
-
-
-
C4
-
-
C5
-
C1
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
C0
-
-
Default
-
D9
D9
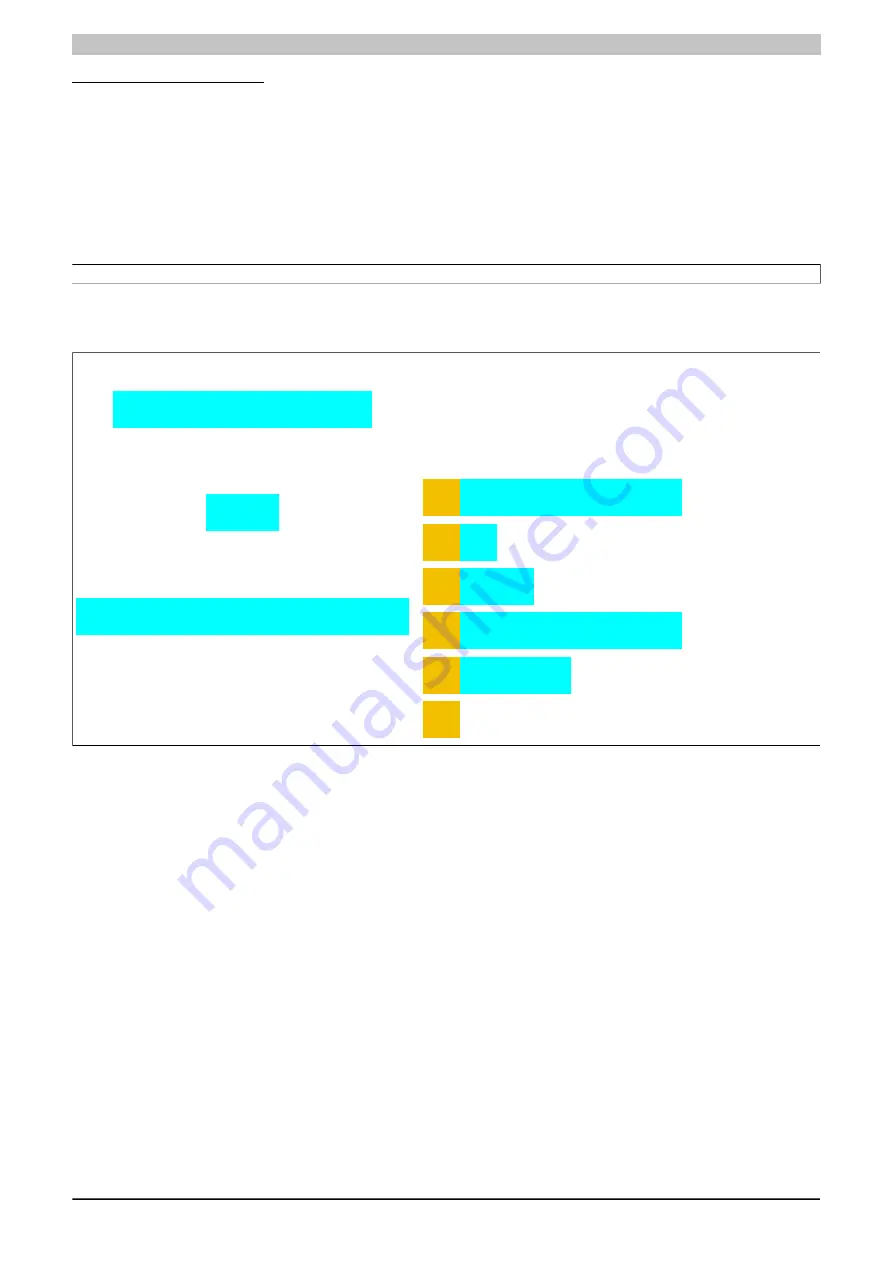
Transmit/Receive array
With 7 USINT elements according to
the configurable MTU size
Figure 76: Transmit/Receive array (default)
First, the messages must be split into segments. In the default configuration, it is important to ensure that each
sequence can hold an entire segment, including the associated control byte. The sequence is limited to the size of
the enable MTU. In other words, a segment must be at least 1 byte smaller than the MTU.
MTU = 7 bytes → Max. segment length = 6 bytes
•
Message 1 (7 bytes)
➯
First segment = Control byte + 6 bytes of data
➯
Second segment = Control byte + 1 byte of data
•
Message 2 (2 bytes)
➯
First segment = Control byte + 2 bytes of data
•
Message 3 (9 bytes)
➯
First segment = Control byte + 6 bytes of data
➯
Second segment = Control byte + 3 data bytes
•
No more messages
➯
C0 control byte