IRF
Internal relay fault indication
<U
CB undervoltage trip coil
TC1
CB trip coil 1
K1
OFF delay time relay
F1
Miniature circuit breaker
In example 3, the fail-safe approach aims at securing motor shutdown via an
emergency switch and in case the control voltage disappears. In case of internal
relay fault, the circuit breaker is tripped via an undervoltage coil after a preset time
delay. The additional time delay allows the relay to recover from the internal fault
situation without tripping the circuit breaker.
<U
TC1
-Q0
BI1
+J02 -A1
+J02 -A1
-A1
-F1
C
Control -
ES
IRF
TO1
TO2
<U
TC1
-Q0
BI1
+J01 -A1
+J01 -A1
-A1
-F1
C
Control -
ES
IRF
TO1
TO2
+J01
+J02
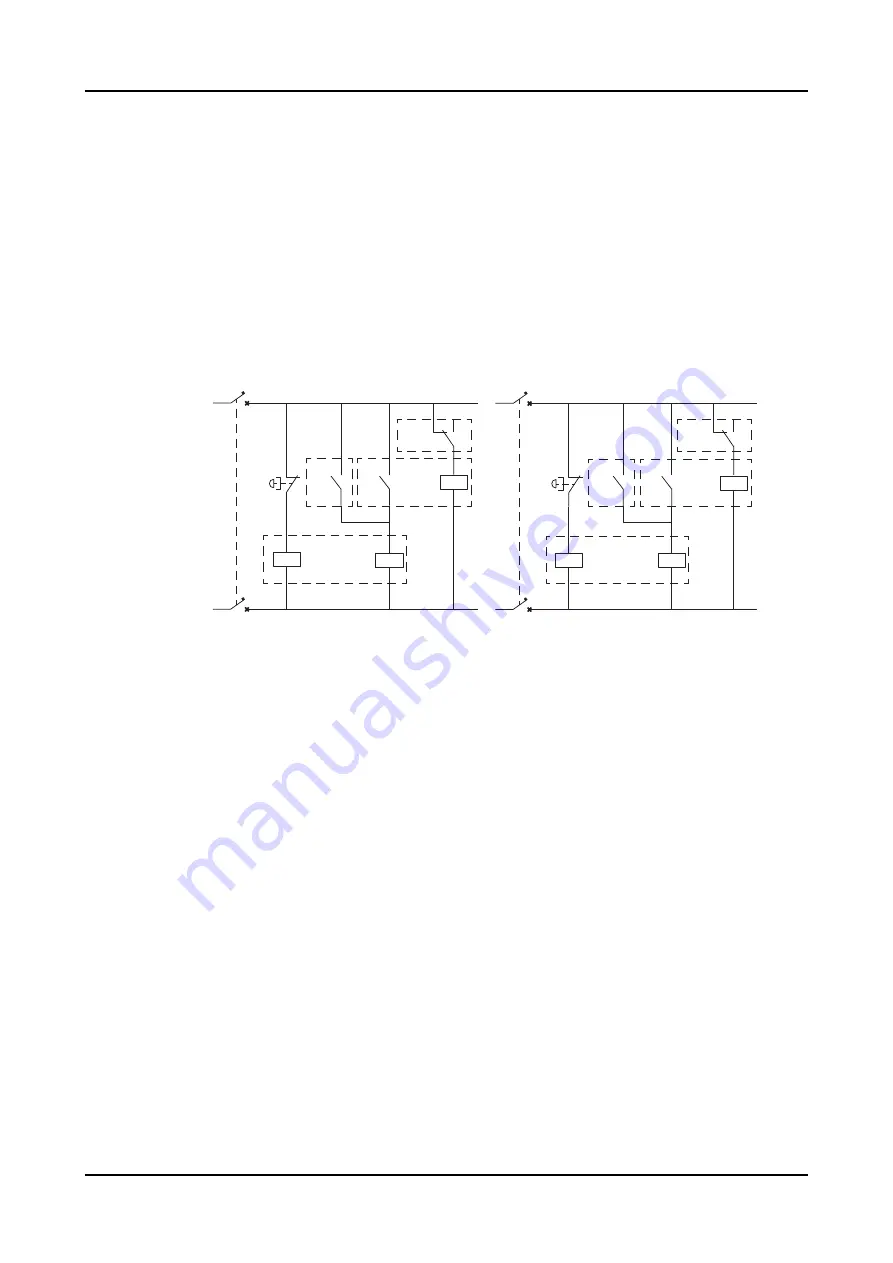
Figure 16: Motor feeder fail-safe trip circuit principle, example 4
J01
Feeder #1 panel
J02
Feeder #2 panel
ES
Emergency stop
Q0
Circuit breaker
TO1
Relay trip output #1
TO2 Relay trip output #2
IRF
Relay internal fault indication
BI1
Relay binary input #1
<U
CB undervoltage trip coil
TC1
CB trip coil 1
F1
Miniature circuit breaker
In example 4, the fail-safe approach aims at securing motor shutdown via an
emergency switch and in case the control voltage disappears. The adjacent panels
provide backup for each other in internal relay fault situations. In case of an internal
relay fault, the situation is noticed by the relay in the adjacent panel and the circuit
breaker in the panel with the faulty relay is tripped after a preset time delay. The
additional time delay allows the relay to recover from the internal fault situation
without tripping the circuit breaker.
1MRS757644 H
Basic functions
620 series
Technical Manual
79






























