S e n d d o c u m e n t a t i o n c o m m e n t s t o m d s f e e d b a c k - d o c @ c i s c o . c o m
1-4
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Command Reference
OL-18089-01, Cisco MDS NX-OS Release 4.x
Chapter 1 CLI Overview
Understanding CLI Command Hierarchy
Understanding CLI Command Hierarchy
The CLI commands are organized hierarchically, with commands that perform similar functions grouped
under the same level. For example, all commands that display information about the system,
configuration, or hardware are grouped under the
show
command, and all commands that allow you to
configure the switch are grouped under the
config terminal
command.
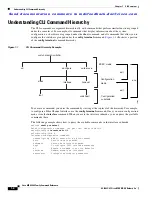
Figure 1-1
illustrates a portion
of the
config terminal
command hierarchy.
Figure 1-1
CLI Command Hierarchy Example
To execute a command, you enter the command by starting at the top level of the hierarchy. For example,
to configure a Fibre Channel interface, use the
config terminal
command. Once you are in configuration
mode, issue the
interface
command. When you are in the interface submode, you can query the available
commands there.
The following example shows how to query the available commands in the interface submode:
switch#
config terminal
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
switch(config)#
interface fc1/1
switch(config-if)#
?
Interface configuration commands:
channel-group Add to/remove from a port-channel
exit Exit from this submode
fcdomain Enter the interface submode
fspf To configure FSPF related parameters
no Negate a command or set its defaults
shutdown Enable/disable an interface
switchport Configure switchport parameters
switch prompt (switch#)
cd
write erase
configure
clock
zoneset
interface
fspf
switchport
EXEC mode
Configuration
mode
Configuration
submode
exit
exit
end
79525