4 - 24
4. HOW TO MONITOR REDUNTANT SYSTEM
4.7 Ethernet Connection
4.7 Ethernet Connection
This section explains the Ethernet connection that connects the GOT to the Ethernet network system.
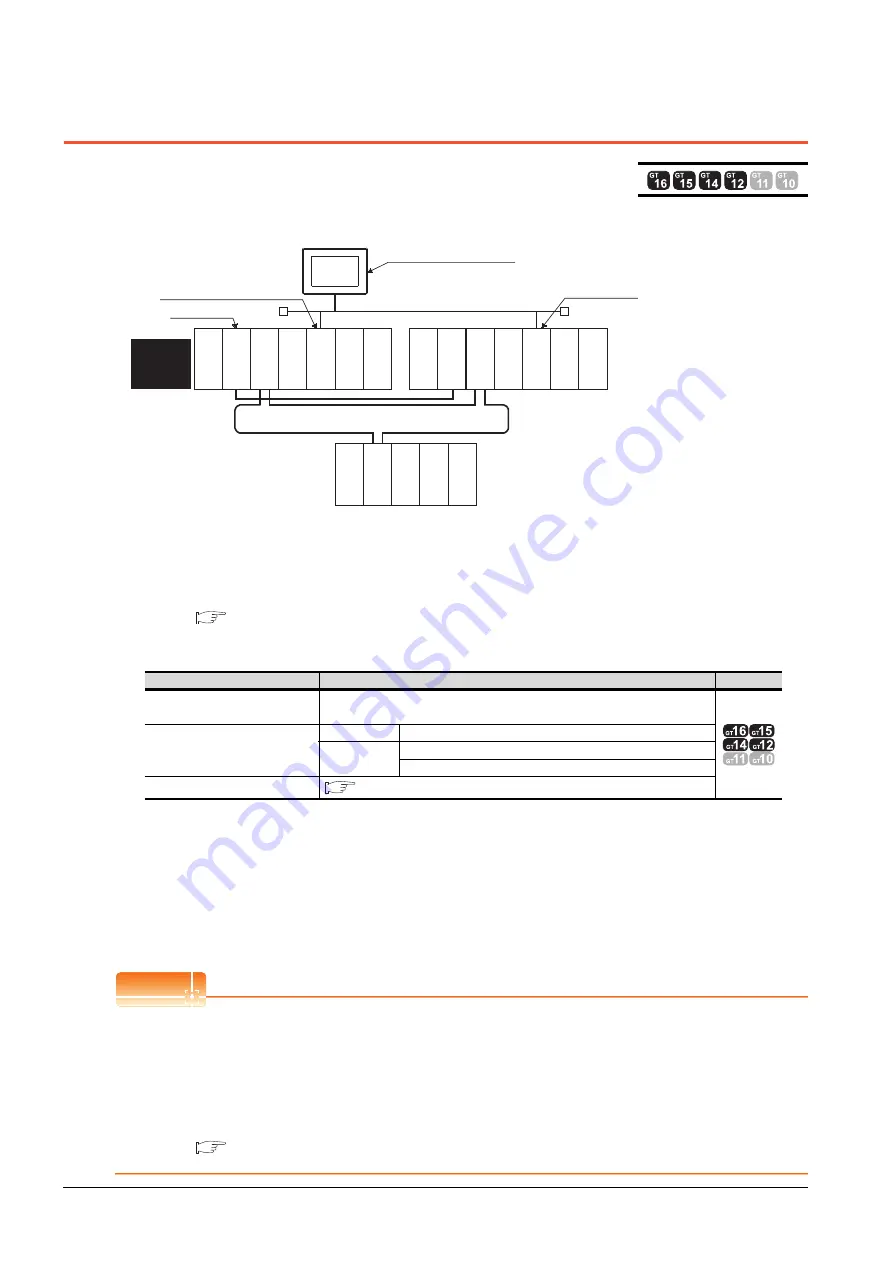
The following shows an example of connecting the GOT to the Ethernet network.
(1) Connection method
Connect the Ethernet network system to the GOT.
Set the Ethernet modules of System A and System B (including NW No., station No, and IP address) to the
Ethernet setting of the GOT side.
For details, refer to the following.
(2) GT Designer3 setting
Set GT Designer3 as follows.
*1
GT14 is not compatible with MELSEC-QS.
To specify the station number which was set in the Q redundant setting in the device setting, set the station
number as the other station.
(3) Monitoring target change when system switching occurs in a redundant system
When system switching occurs, Ethernet module station No. 2 takes over the control of the Ethernet network
system as the control system.
Since the GOT monitors the control system, he monitoring target is automatically changed to the Ethernet
module station No. 2.
POINT
POINT
POINT
When monitoring control system without Q redundant setting (Only GT16, GT15 and GT14)
When system switching occurs, Ethernet module station No. 2 takes over the control of the Ethernet network
system as the control system.
Since the GOT monitors the station of the specified station number, the monitoring target cannot be changed to the
station No. 2 in response to the system switching.
As a countermeasure, create a screen to monitor the PLC CPU of the control system by switching the station
numbers between System A and System B using the script function.
4.10 Switch the Monitor Target to the Control System Using the Script Function
Setting item
Settings
Model
Controller Type
GT16, GT15, GT12: MELSEC-QnA/Q/QS, MELDAS C6*
GT14: MELSEC-QnA/Q, MELDAS C6*
*1
Device setting (Network setting)
Host
Host (The control system is monitored.)
Other
NW No.: Network No. of Ethernet
Station No.: Station number of the control system
Q Redundant Setting
Monitor target
MELSECNET/H remote I/O network
Po
w
e
r
s
up
pl
y
mo
d
u
le
Em
pt
y
GOT
Network No. 1, Station No. 1
Control
system
(System A)
Em
pt
y
Q25PRHCPU
QJ71LP21-25
QJ71BR1
1
QJ71E71-100
QJ61BT1
1N
Em
pt
y
Standby
system
(System B)
Q25PRHCPU
QJ71LP21-25
QJ71BR1
1
QJ71E71-100
QJ61BT1
1N
QJ72LP25-25
QJ71C24N
Network No. 1, Station No. 3
Network No. 1,
Station No. 2
Ethernet
Pow
e
r
s
up
pl
y
mo
d
u
le
Po
w
e
r
s
up
pl
y
mo
d
u
le
Em
pt
y
Summary of Contents for GT15
Page 2: ......
Page 34: ...A 32 ...
Page 92: ......
Page 110: ...2 18 2 DEVICE RANGE THAT CAN BE SET 2 9 MELSEC WS ...
Page 186: ...5 10 5 BUS CONNECTION 5 2 System Configuration ...
Page 218: ...5 42 5 BUS CONNECTION 5 4 Precautions ...
Page 254: ...6 36 6 DIRECT CONNECTION TO CPU 6 6 Precautions ...
Page 286: ...7 32 7 COMPUTER LINK CONNECTION 7 6 Precautions ...
Page 350: ...8 64 8 ETHERNET CONNECTION 8 5 Precautions ...
Page 368: ...9 18 9 MELSECNET H CONNECTION PLC TO PLC NETWORK 9 5 Precautions ...
Page 420: ...11 26 11 CC Link IE CONTROLLER NETWORK CONNECTION 11 5 Precautions ...
Page 440: ...12 20 12 CC Link IE FIELD NETWORK CONNECTION 12 5 Precautions ...
Page 490: ...13 50 13 CC Link CONNECTION INTELLIGENT DEVICE STATION 13 5 Precautions ...
Page 510: ......
Page 564: ...15 54 15 INVERTER CONNECTION 15 7 Precautions ...
Page 668: ......
Page 712: ...21 12 21 MULTIPLE GT14 GT12 GT11 GT10 CONNECTION FUNCTION 21 5 Precautions ...
Page 713: ...MULTI CHANNEL FUNCTION 22 MULTI CHANNEL FUNCTION 22 1 ...
Page 714: ......
Page 760: ...22 46 22 MULTI CHANNEL FUNCTION 22 5 Multi channel Function Check Sheet ...
Page 761: ...FA TRANSPARENT FUNCTION 23 FA TRANSPARENT FUNCTION 23 1 ...
Page 762: ......
Page 860: ...REVISIONS 4 ...
Page 863: ......
















































