5-198
F60 Feeder Protection System
GE Multilin
5.6 GROUPED ELEMENTS
5 SETTINGS
5
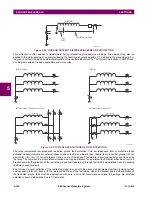
Figure 5–82: RGF AND PERCENT DIFFERENTIAL ZONES OF PROTECTION
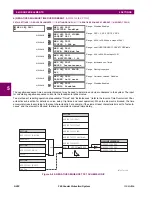
This protection is often applied to transformers having impedance-grounded wye windings. The element may also be
applied to the stator winding of a generator having the neutral point grounded with a CT installed in the grounding path, or
the ground current obtained by external summation of the neutral-side stator CTs. The
Typical Applications of RGF Protec-
tion
diagram explains the basic application and wiring rules.
Figure 5–83: TYPICAL APPLICATIONS OF RGF PROTECTION
The relay incorporates low-impedance restricted ground fault protection. This low-impedance form of protection faces
potential stability problems. An external phase-to-phase fault is an ultimate case. Ideally, there is neither ground (IG) nor
neutral (IN = IA + IB + IC) current present. If one or more of the phase CTs saturate, a spurious neutral current is seen by
the relay. This is similar to a single infeed situation and may be mistaken for an internal fault. Similar difficulties occur in a
breaker-and-a-half application of the restricted ground fault, where any through fault with a weak infeed from the winding
itself may cause problems.
The UR uses a novel definition of the restraining signal to cope with the above stability problems while providing for fast
and sensitive protection. Even with the improved definition of the restraining signal, the breaker-and-a-half application of
the restricted ground fault must be approached with care, and is not recommended unless the settings are carefully
selected to avoid maloperation due to CT saturation.
842731A1.CDR
35%
RGF
ZONE
DIFFERENTIAL ZONE
Rg
WINDING
842732A1.CDR
IG
IG
IA
IA
IB
IB
IC
IC
2
1
2
1
2
1
IG
IG
Transformer Winding
Transformer Winding
(A) Transformer
(B) Transformer in a Breaker-and-a-Half
(C) Stator
(D) Stator without a Ground CT
Stator Winding
Stator Winding
IA
IA
IA
IA
IB
IB
IB
IB
IC
IC
IC
IC
Summary of Contents for F60
Page 10: ...x F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin TABLE OF CONTENTS ...
Page 30: ...1 20 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 1 5 USING THE RELAY 1 GETTING STARTED 1 ...
Page 138: ...4 28 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 4 2 FACEPLATE INTERFACE 4 HUMAN INTERFACES 4 ...
Page 454: ...5 316 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 5 10 TESTING 5 SETTINGS 5 ...
Page 500: ...7 14 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 7 1 COMMANDS 7 COMMANDS AND TARGETS 7 ...
Page 508: ...8 8 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 8 2 FAULT LOCATOR 8 THEORY OF OPERATION 8 ...
Page 522: ...10 12 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin 10 6 DISPOSAL 10 MAINTENANCE 10 ...
Page 660: ...B 116 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin B 4 MEMORY MAPPING APPENDIX B B ...
Page 706: ...E 10 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin E 1 IEC 60870 5 104 APPENDIX E E ...
Page 718: ...F 12 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin F 2 DNP POINT LISTS APPENDIX F F ...
Page 728: ...H 8 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin H 2 ABBREVIATIONS APPENDIX H H Z Impedance Zone ...
Page 730: ...H 10 F60 Feeder Protection System GE Multilin H 3 WARRANTY APPENDIX H H ...