5238-E P-167
SECTION 8 LATHE AUTO-PROGRAMMING FUNCTION (LAP)
SECTION 8 LATHE AUTO-PROGRAMMING FUNCTION
(LAP)
1.
Overview
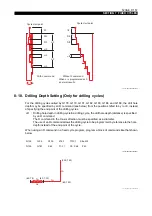
LAP (Lathe Auto-Programming) is a function to make full use of high-speed processing capability
which characterizes the NC. With this function, the control automatically generates a tool path to
produce the required part contour.
When this function is used, a program comprising the dimension data of the final contour to be
finished, including rough cut conditions, is prepared as the Contour Definition Program; when it is
called out with the cutting conditions specified, the control automatically generates the tool path for
the rough cut cycles, and then finishes the workpiece to the programmed dimensions.
This feature permits the programmer to complete part programs by simply picking up the
dimensions specified in an engineering drawing. It not only simplifies programming but also
reduces programming time; it also makes the preparatory steps for programming easier, as well as
the program check procedure.
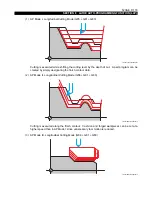
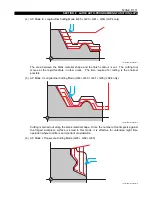
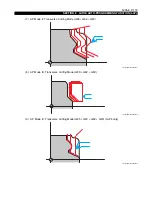
Various cutting modes available with the LAP can cope with any intended type of cutting.
In addition to the features above, LAP4 (see note) is also available; with LAP4, a workpiece can be
cut using the most efficient tool paths by simply entering the blank workpiece shape.
Features of LAP:
•
No special programming language is needed. The same methods as used in conventional
programming also apply for the LAP function.
•
Programming time can be greatly reduced.
•
Programming for rough cut cycles can be eliminated, and this simplifies manual calculation in
programming.
•
Change of cutting conditions, such as depth of cut and feedrate, is possible during a rough cut
cycle.
•
By entering the blank workpiece shape, unnecessary air-cutting tool paths can be eliminated to
improve cutting efficiency (LAP4).
Note: LAP4 has been developed by extending the functions of LAP3.