9 Positioning Control
9.8 Multi-Speed Operation
173
FX
3U
-20SSC-H Positioning Block User's Manual
1
Int
roduct
ion
2
Sy
stem
conf
igur
ati
on
3
Exam
ple
C
onnect
ion
4
Ins
tall
a
tion
5
Wi
rin
g
6
Me
m
o
ry
confi
gur
at
ion
and da
ta
7
Befor
e
star
ting
positi
oning
contr
o
l
8
M
anual c
ont
ro
l
9
Posit
ioni
ng
C
ont
rol
10
Table O
per
at
ion
POINT
• In multi-speed operation, preparation for the next table number operation is performed simultaneously with
the current operation.
If a travel distance to shift the operation speed is less than the pulses to accelerate/decelerate, or if the
travel time is too short (at 50 ms or less), the current operation does not continue and temporarily stops.
• When using m code in multi-speed operation, use the With mode.
With the m code in After mode, operation does not continue from the table since the 20SSC-H suspends
the operation shift to the next table until the m code turns OFF .
• Multi-speed operation ends if another operation information is performed during the multi-speed operation.
• Multi-speed operation operates independently in the X-axis and the Y-axis.
Even if performing multi-speed operation using XY-axes table information, only the setup for X-axis multi-
speed operation or Y-axis multi-speed operation is used.
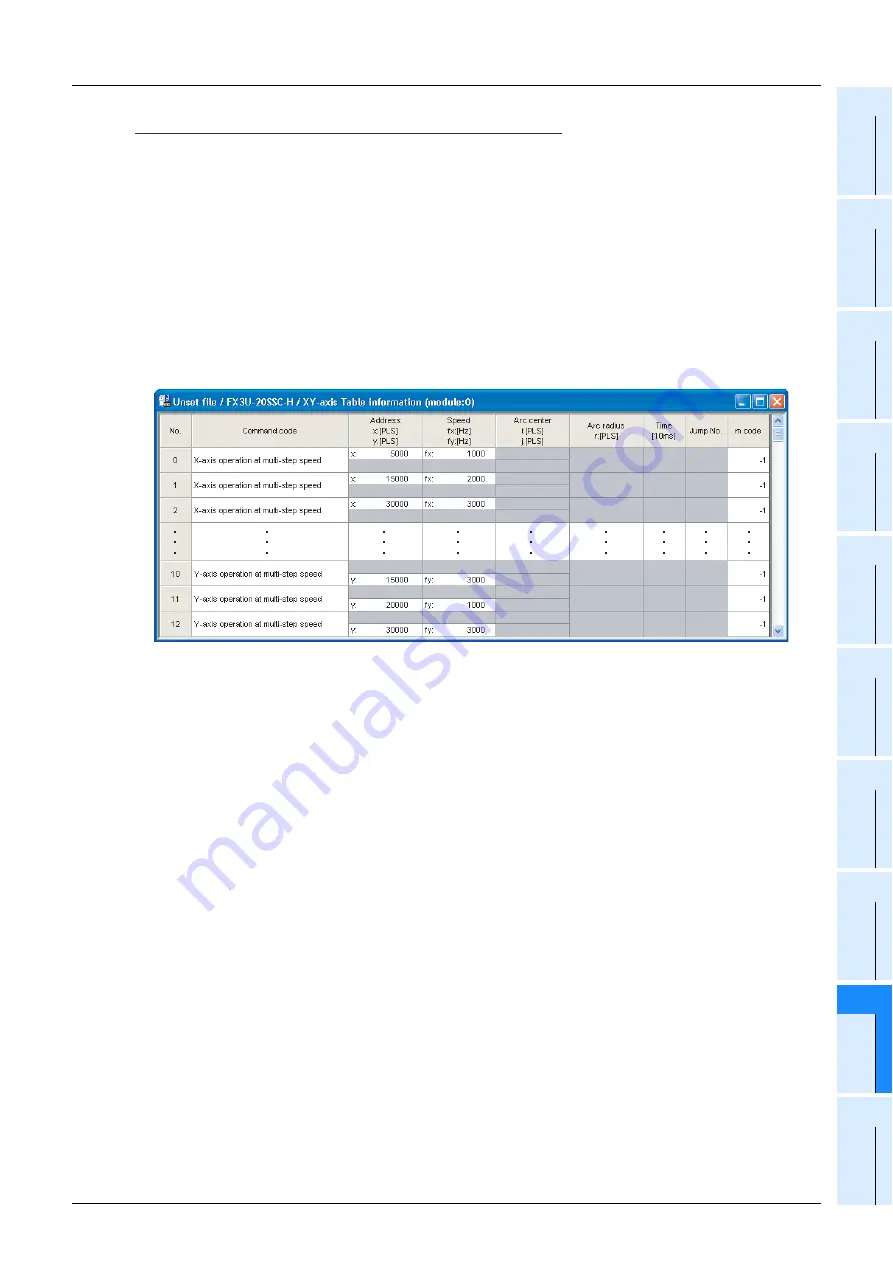
Setting example of XY-axes table information
2. Operation information
Set multi-speed operation, absolute address specification, relative address specification and the End
command in the operation information.
→
For details, refer to Chapter 10
3. Speed information
The actual operation speed is "operation speed 1
×
override setting."
Operation speed 1 can be changed using the operation speed change function except under the following
conditions.
→
For change of the operation speed, refer to Section 7.6
• During deceleration operation
• When the speed change disable during operation signal is ON.
4. Position (address) information
The absolute/relative address can be specified in the operation information.
With the specified absolute address: Specifies a target address (position) using address 0 as the base.
With the specified relative address: Specifies a travel amount from the current address.
5. Rotation Direction
With the specified absolute address: The rotation direction depends on whether the position (address)
information is larger or smaller than the current address.
With the specified relative address: The rotation direction is decided by the sign (positive/negative) of
position (address) information.















































