4-177
(b) PID control with differential feedback:
(10-03 = 2, 4)
P
I
Control
D
+
-
+
+
+
+
Feedback
Set Value
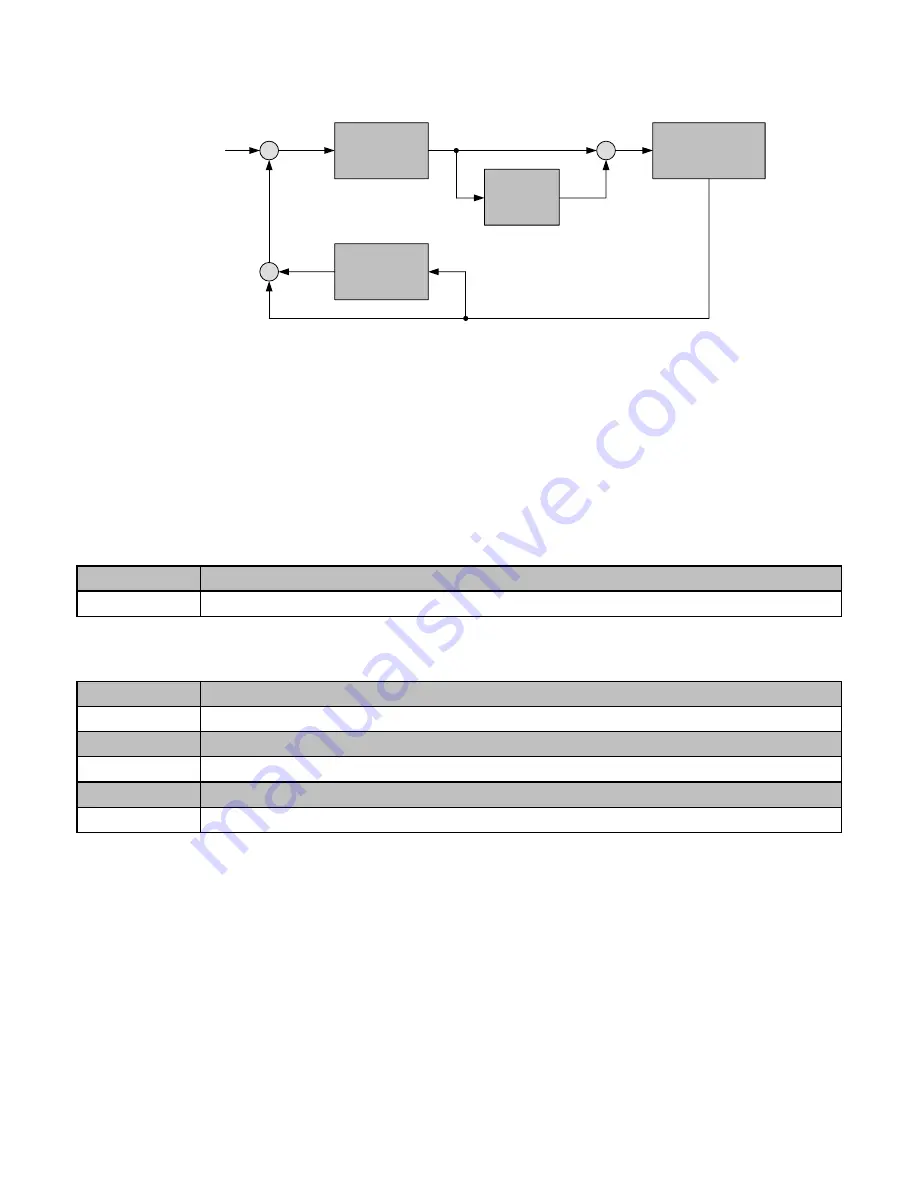
Figure 4.3.80c PID control for feedback differential value
Feedback (detected value) is derivative controlled and set by parameter 10-07.
Make sure to adjust the PID parameters without causing system instability. Refer to Figure 4.3.9 for PID control
for feedback value differential.
For 10-03 = 1 or 2, if the error signal (target minus feedback) is positive, the output frequency increases and vice
versa.
For 10-03 = 3 or 4, if the error signal (target minus feedback) is positive, the output frequency decreases and vice
versa.
10-04
Feedback gain
Range
【
0.01~10.00
】
Parameter 10-04 sets the feedback calibration gain.
10-05
Proportional gain (P)
Range
【
0.00~10.00
】
10-06
Integral time (I)
Range
【
0.0~100.0
】
Sec
10-07
Differential time (D)
Range
【
0.00~10.00
】
Sec
PID Adjustments
10-05 Proportional Gain control:
The error signal (deviation) between the input command (set value) and the
actual control value (feedback). This error signal or deviation is amplified by the proportional gain (P) to control
the offset between the set value and the feedback value.
10-06 Integral control:
The output of this control is the integral of the error signal (difference between set value
and feedback value) and is used to minimize the offset signal that is left over from the gain control. When the
integral time (I) is increased, the system response becomes slower.
10-07 Differential control:
This control is the inverse from integral control and tries to guess the behavior of the
error signal by multiplying the error with the differential time. The result is added to the PID input. Differential
control slows down the PID controller response and may reduce system oscillation.
Note:
Most applications that






























