ADVANCED APPLICATION OPTIONS
Multi-Drive Configurations
109
Jockey:
A Jockey is used to maintain system pressure in a low situation. Refer to
•
In a multi-drive system, the Jockey VFD ID is always the last one in the sequence and does not change
roles during system alternation.
•
During normal operation with high demand, the Jockey will function like the last ID Lag if required to
maintain pressure. It will be the last to start and the first to stop.
•
During low demand operation, the Lead drive will act as the Main for regular Jockey control.
Sequence Assignment
The system rotates drive roles through the network based on the parameter setting
Alternation [ADV–45]
.
There are three possible scenarios:
Alternation–Disabled:
This setting might be appropriate when the system primarily operates at a low flow
rate and uses the Lag pumps as backups when needed.
•
In this case, the Lead pump could be sized for efficiency at a lower flow rate and would always be the
first to start.
•
The Lead/Master would regulate the pressure of the system using its own PID sensor.
•
The Lag pumps could be sized differently and could either use their own PID or be set to run at a spe
-
cific frequency.
Alternation–Timer:
This scenario might be used to rotate the Lead role to distribute wear on a system with
continuous operation.
•
In this case, the roles would be rotated after running for a specific time, set in
Alternation TMR [ADV–46]
.
•
In addition to balancing usage, this practice would help ensure the proper functioning of Lag units that
might otherwise be idle for extended periods.
•
The best practice would be to size and program all pumps/drives the same.
Alternation–Master Power-Up:
For a system that is stopped and started on a periodic basis, such as a man
-
ufacturing plant, it might be desirable to rotate system roles to maintain consistent performance.
•
In this case, the Lead changes each time the system is activated (Master is power cycled).
In all cases, the Master will be the drive with the lowest ID number
[ADV–37]
. If the Master faults, is switched
to
Hand
, or is set to
1_Skip it
in
Set VFD Ready [ADV–47]
, the role is shifted to the drive with the next lowest ID. If
there is a break in communication, the lowest ID on any remaining functional network assumes the Master
role.
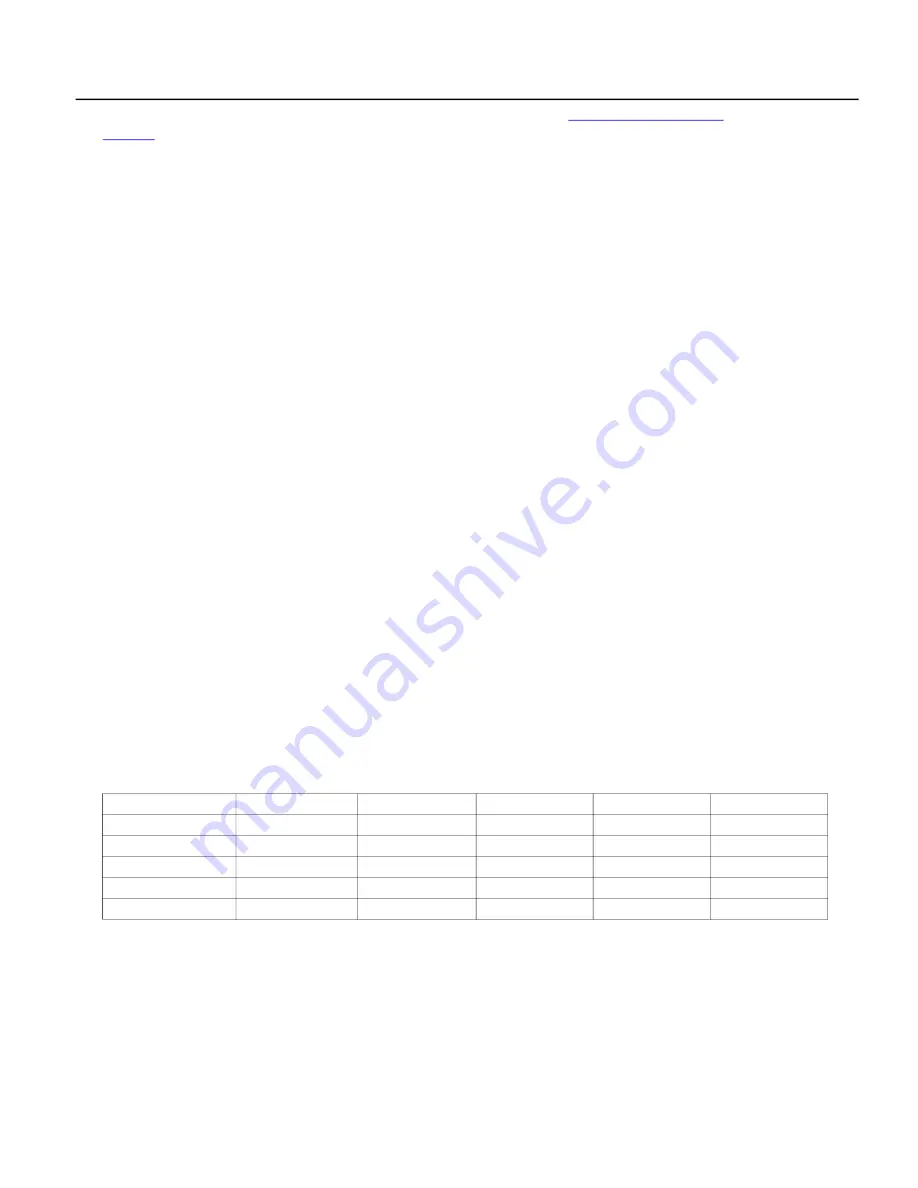
Example Rotation Pattern
Fault Handling
If a fault occurs on a Lead or Lag drive, the Master will remove the drive from the sequence, rotate the Lead/
Lag roles of the remaining drives, and initiate a start command for the next drive in sequence.
If any drive detects an Over Pressure, Broken Pipe, or Pipe Leak fault, it communicates the condition to the
Master, which then stops operation of the entire system. All other faults are local to an individual drive.
Event
VFD 1
VFD 2
VFD 3
VFD 4
VFD 5
System Start
Master/Lead
Lag 1
Lag 2
Lag 3
Standby 1
First Alternation
Master/Lag 3
Lead
Lag 1
Lag 2
Standby 1
Second Alternation
Master/Lag 2
Lag 3
Lead
Lag 1
Standby 1
VFD 1 Fault
Standby 1
Master/Lag 3
Lead
Lag 1
Lag 2
Next Alternation
Standby 1
Master/Lag 2
Lag 3
Lead
Lag 1
Summary of Contents for CERUS X-DRIVE CXD-003A-4V
Page 2: ......
Page 3: ...CERUS X DRIVE INSTALLATION AND OPERATION MANUAL Firmware Version 1 2 Franklin Electric Co Inc ...
Page 96: ...OPERATION Protection Features 96 ...
Page 112: ...ADVANCED APPLICATION OPTIONS Multi Drive Configurations 112 ...
Page 124: ...COMMUNICATIONS BACnet Communication 124 ...
Page 128: ...ACCESSORIES Optional Extension Cards 128 Frame D Frame E Frame F ...
Page 129: ...ACCESSORIES Optional Extension Cards 129 Frame G Frame H ...
Page 132: ...ACCESSORIES Optional Extension Cards 132 ...
Page 234: ...PARAMETER REFERENCE TABLES Parameter Descriptions Motor Menu 234 ...
Page 250: ...GLOSSARY 250 ...
















































