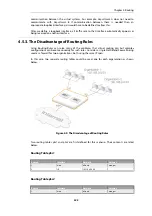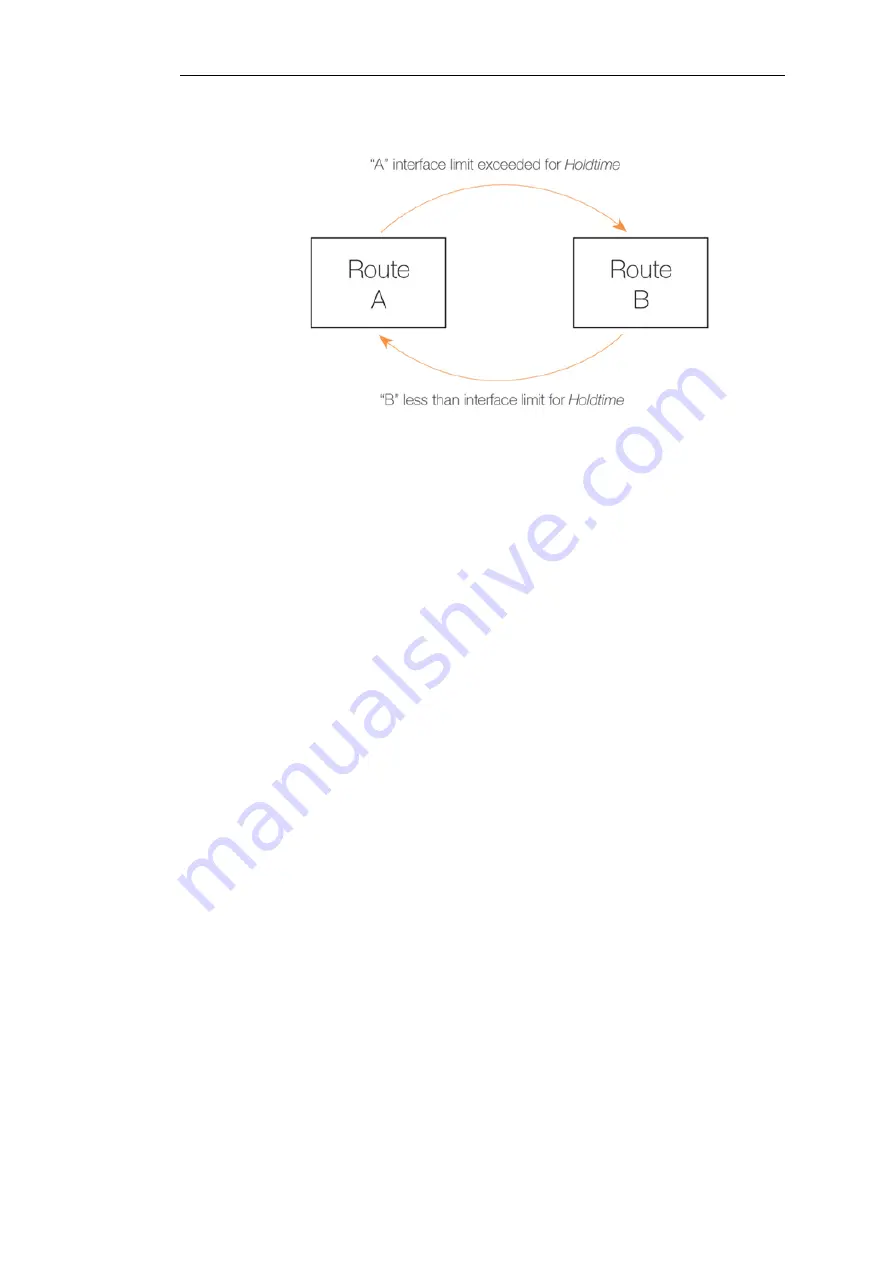
Figure 4.6. The RLB Spillover Algorithm
Spillover Limits
are set separately for ingoing and outgoing traffic with only one of these
typically being specified. If both are specified then only one of them needs to be
exceeded continuously for
Hold Timer
seconds for the next matching route to be chosen.
The units of the limits, such as Mbps, can be selected to simplify specification of the
values.
Using Route Metrics with Round Robin
An individual route has a
metric
associated with it, with the default metric value being zero.
With the
Round Robin
and the associated
Destination
algorithms, the
metric
value can be set
differently on matching routes to create a bias towards the routes with lower metrics. Routes
with lower metrics will be chosen more frequently than those with higher metrics and the
proportion of usage will be based on the relative differences between the metrics of matching
routes.
In a scenario with two ISPs, if the requirement is that the bulk of traffic passes through one of the
ISPs then this can be achieved by enabling RLB and setting a low metric on the route to the
favoured ISP. A relatively higher metric is then set on the route to the other ISP.
Using Route Metrics with Spillover
When using the
Spillover
algorithm, a number of points should be noted regarding metrics and
the way alternative routes are chosen:
•
Route metrics should always be set.
With spillover, NetDefendOS always chooses the route in the matching routes list that has the
lowest metric. The algorithm is not intended to be used with routes having the same metric
so the administrator should set different metrics for all the routes to which spillover applies.
Metrics determine a clear ordering for which route should be chosen next after the interface
traffic limits for the chosen route have been exceeded.
•
There can be many alternative routes.
Several alternative routes can be set up, each with their own interface limits and each with a
Chapter 4: Routing
318
Summary of Contents for NetDefendOS
Page 30: ...Figure 1 3 Packet Flow Schematic Part III Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 30 ...
Page 32: ...Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 32 ...
Page 144: ...Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 144 ...
Page 284: ...Chapter 3 Fundamentals 284 ...
Page 392: ...Chapter 4 Routing 392 ...
Page 419: ... Host 2001 DB8 1 MAC 00 90 12 13 14 15 5 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 419 ...
Page 420: ...Chapter 5 DHCP Services 420 ...
Page 573: ...Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 573 ...
Page 607: ...Chapter 7 Address Translation 607 ...
Page 666: ...Chapter 8 User Authentication 666 ...
Page 775: ...Chapter 9 VPN 775 ...
Page 819: ...Chapter 10 Traffic Management 819 ...
Page 842: ...Chapter 11 High Availability 842 ...
Page 866: ...Default Enabled Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 866 ...
Page 879: ...Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 879 ...