Example 4.9. Setting Up RLB
In this example, the details of the RLB scenario described above will be implemented. The
assumption is made that the various IP address book objects needed have already been defined.
The IP objects WAN1 and WAN2 represent the interfaces that connect to the two ISPs and the IP
objects GW1 and GW2 represent the IP addresses of the gateway routers at the two ISPs.
Step 1. Set up the routes in the main routing table
Step 2. Create an RLB Instance object
A Route Load Balancing Instance object is now created which uses the
Destination
algorithm will
be selected to achieve stickiness so the server always sees the same source IP address (
WAN1
or
WAN2
) from a single client.
Command-Line Interface
gw-world:/> add RouteBalancingInstance main Algorithm=Destination
Web Interface
1.
Go to: Network > Routing > Instances > Add > Route Balancing Instance
2.
The route balancing instance dialog will appear. Now select:
•
Routing Table: main
•
Algorithm: Destination
•
Click OK
Step 3. Create IP rules to allow traffic to flow
Finally, IP rules needed to be added to an IP rule set to allow traffic to flow. The detailed steps for
this are not included here but the created rules would follow the pattern described above.
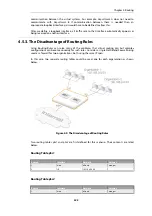
RLB with VPN
When using RLB with VPN, a number of issues need to be overcome.
If we were to try and use RLB to balance traffic between two IPsec tunnels, the problem that
arises is that the
Remote Endpoint
for any two IPsec tunnels in NetDefendOS must be different.
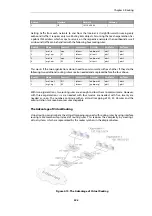
The solutions to this issue are as follows:
•
Use two ISPs, with one tunnel connecting through one ISP and the other tunnel connecting
through the other ISP. RLB can then be applied as normal with the two tunnels.
In order to get the second tunnel to function in this case, it is necessary to add a single host
route in the
main
routing table that points to the secondary ISPs interface and with the
secondary ISPs gateway.
This solution has the advantage of providing redundancy should one ISP link fail.
•
Use VPN with one tunnel that is IPsec based and another tunnel that is uses a different
protocol.
Chapter 4: Routing
321
Summary of Contents for NetDefendOS
Page 30: ...Figure 1 3 Packet Flow Schematic Part III Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 30 ...
Page 32: ...Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 32 ...
Page 144: ...Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 144 ...
Page 284: ...Chapter 3 Fundamentals 284 ...
Page 392: ...Chapter 4 Routing 392 ...
Page 419: ... Host 2001 DB8 1 MAC 00 90 12 13 14 15 5 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 419 ...
Page 420: ...Chapter 5 DHCP Services 420 ...
Page 573: ...Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 573 ...
Page 607: ...Chapter 7 Address Translation 607 ...
Page 666: ...Chapter 8 User Authentication 666 ...
Page 775: ...Chapter 9 VPN 775 ...
Page 819: ...Chapter 10 Traffic Management 819 ...
Page 842: ...Chapter 11 High Availability 842 ...
Page 866: ...Default Enabled Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 866 ...
Page 879: ...Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 879 ...