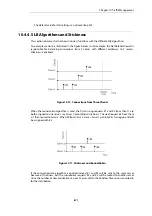
•
The destination MAC address is the Ethernet multicast address corresponding to the shared
hardware address and this has the form:
11-00-00-00-nn-mm
Where
nn
is a bit mask made up of the interface bus, slot and port on the master and
mm
represents the cluster ID,
Link layer multicasts are used over normal unicast packets for security. Using unicast packets
would mean that a local attacker could fool switches to route heartbeats somewhere else so
the inactive system never receives them.
Failover Time
The time for failover is typically about one second which means that clients may experience a
failover as a slight burst of packet loss. In the case of TCP, the failover time is well within the
range of normal retransmit timeouts so TCP will retransmit the lost packets within a very short
space of time, and continue communication. UDP does not allow retransmission since it is
inherently an unreliable protocol.
Shared IP Addresses and ARP
Both master and slave know about the shared IP address. ARP queries for the shared IP address,
or any other IP address published via the ARP configuration section or through Proxy ARP, are
answered by the active system.
The hardware address of the shared IP address and other published addresses are not related to
the actual hardware addresses of the interfaces. Instead the MAC address is constructed by
NetDefendOS from the Cluster ID in the form
11-00-00-C1-4A-nn
where
nn
is derived by
combining the configured Cluster ID with the hardware bus/slot/port of the interface. The
Cluster ID must be unique for each NetDefendOS cluster in a network.
As the shared IP address always has the same hardware address, there will be no latency time in
updating ARP caches of units attached to the same LAN as the cluster when failover occurs.
When a cluster member discovers that its peer is not operational, it broadcasts gratuitous ARP
queries on all interfaces using the shared hardware address as the sender address. This allows
switches to re-learn within milliseconds where to send packets destined for the shared address.
The only delay in failover therefore, is detecting that the active unit is down.
ARP queries are also broadcast periodically to ensure that switches do not forget where to send
packets destined for the shared hardware address.
Promiscuous Mode
The Ethernet interfaces in an HA cluster must operate in
promiscuous mode
for HA to function.
This mode means that traffic with a destination MAC address that does not match the Ethernet
interface's MAC address will be sent to NetDefendOS and not discarded by the interface.
Promiscuous mode is enabled automatically by NetDefendOS and the administrator does not
need to worry about doing this.
If the administrator enters a CLI command
ifstat <ifname>
, the
Receive Mode
status line will show
the value
Promiscuous
next to it instead of
Normal
to indicate the mode has changed. This is
discussed further in
Section 3.4.2, “Ethernet Interfaces”
HA with Anti-Virus and IDP
Chapter 11: High Availability
824
Summary of Contents for NetDefendOS
Page 30: ...Figure 1 3 Packet Flow Schematic Part III Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 30 ...
Page 32: ...Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 32 ...
Page 144: ...Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 144 ...
Page 284: ...Chapter 3 Fundamentals 284 ...
Page 392: ...Chapter 4 Routing 392 ...
Page 419: ... Host 2001 DB8 1 MAC 00 90 12 13 14 15 5 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 419 ...
Page 420: ...Chapter 5 DHCP Services 420 ...
Page 573: ...Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 573 ...
Page 607: ...Chapter 7 Address Translation 607 ...
Page 666: ...Chapter 8 User Authentication 666 ...
Page 775: ...Chapter 9 VPN 775 ...
Page 819: ...Chapter 10 Traffic Management 819 ...
Page 842: ...Chapter 11 High Availability 842 ...
Page 866: ...Default Enabled Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 866 ...
Page 879: ...Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 879 ...