A brute force attack is characterized by an external computer connecting to an authenticating
device over a network and then repeatedly trying different username/password pairs in rapid
succession. This type of attack relies on being able to try many combinations in a short period of
time and NetDefendOS neutralizes this approach by forcing progressively longer waiting time
between successive sets of attempts.
If the first few username/password validation attempts fail, there is a small wait before the next
attempt can be made. If the next few attempts also fail, there is a longer wait imposed before the
next attempt can be made and so on. The increasing wait times make it impractical to try enough
credential combinations in order to find a valid one. However, a valid user who simply mistyped
their credentials more than once should still be able to be authenticated within a reasonable
amount of time.
The Blocked User List
When a certain number of initial username/password validation attempts fail, NetDefendOS will
add the user to a "blocked user list" and they will remain on the list until a NetDefendOS
reconfigure or restart. A user on this list has an integer property called
Blocked remaining
which is
a decrementing number of seconds. While
Blocked remaining
is greater than zero, NetDefendOS
will not try to authenticate new validation attempts. This number will be reset to a new positive
value after another failed authentication attempt.
If the
Blocked remaining
value reaches zero, the user will not be removed from the list for 24
hours, and this allows the administrator to see such blocked users later. However, a
Blocked
remaining
value of zero means that the user can try to make another authentication attempt
which NetDefendOS will not ignore.
How the User Experiences Brute Force Protection
Even when a user is on the blocked list, they will be allowed to make further validation attempts
as though nothing had changed. In other words, even if their credentials are correct,
NetDefendOS will treat those attempts as failed until the
Blocked remaining
value reaches zero.
There will be no indication to the user that they are on the blocked list or how long they must
wait. Likewise, a malicious attacker will also get no feedback from NetDefendOS about why
attempts are failing.
Monitoring the Blocked List
NetDefendOS provides the following methods for examining the users who have been placed on
the blocked user list:
•
CLI
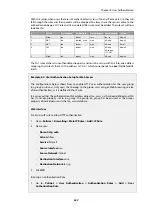
The
userauth
CLI command can be used to provide information about blocked users:
userauth -list -verbose -blocked
Blocked users:
User
Local Database
Blocked since
Blocked remaining
-------------- --------------- -------------------- --------------------
clavu
sslvpn
2016-06-10 12:09:18
17s
Note that the
blocked remaining
message indicates how long that user must wait before their
credentials will be accepted.
•
Web Interface
The information shown above from the CLI is also available in the NetDefendOS Web
Chapter 8: User Authentication
631
Summary of Contents for NetDefendOS
Page 30: ...Figure 1 3 Packet Flow Schematic Part III Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 30 ...
Page 32: ...Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 32 ...
Page 144: ...Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 144 ...
Page 284: ...Chapter 3 Fundamentals 284 ...
Page 392: ...Chapter 4 Routing 392 ...
Page 419: ... Host 2001 DB8 1 MAC 00 90 12 13 14 15 5 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 419 ...
Page 420: ...Chapter 5 DHCP Services 420 ...
Page 573: ...Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 573 ...
Page 607: ...Chapter 7 Address Translation 607 ...
Page 666: ...Chapter 8 User Authentication 666 ...
Page 775: ...Chapter 9 VPN 775 ...
Page 819: ...Chapter 10 Traffic Management 819 ...
Page 842: ...Chapter 11 High Availability 842 ...
Page 866: ...Default Enabled Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 866 ...
Page 879: ...Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 879 ...