gw-world:/> pipe -u <pipename>
can be used to display a list of currently active users in each pipe.
10.1.9. A Summary of Traffic Shaping
NetDefendOS traffic shaping provides a sophisticated set of mechanisms for controlling and
prioritizing network packets. The following points summarize its use:
•
Select the traffic to manage through
Pipe Rules
.
•
Pipe Rules send traffic through
Pipes
.
•
A pipe can have a limit which is the maximum amount of traffic allowed.
•
A pipe can only know when it is
full
if a total limit for the pipe is specified.
•
A single pipe should handle traffic in only one direction (although 2 way pipes are allowed).
•
Pipes can be chained so that one pipe's traffic feeds into another pipe.
•
Specific traffic types can be given a
priority
in a pipe.
•
Priorities can be given a maximum limit which is also a guarantee. Traffic that exceeds this
will be sent at the minimum precedence which is also called the
Best Effort
precedence.
•
At the best effort precedence all packets are treated on a "first come, first forwarded" basis.
•
Within a pipe, traffic can also be separated on a
Group
basis. For example, by source IP
address. Each user in a group (for example, each source IP address) can be given a maximum
limit and precedences within a group can be given a limit/guarantee.
•
A pipe limit need not be specified if group members have a maximum limit.
•
Dynamic Balancing
can be used to specify that all users in a group get a fair and equal
amount of bandwidth.
10.1.10. More Pipe Examples
This section looks at some more scenarios and how traffic shaping can be used to solve particular
problems.
A Basic Scenario
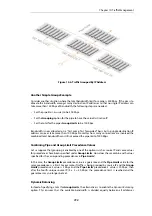
The first scenario will examine the configuration shown in the image below, in which incoming
and outgoing traffic is to be limited to 1 megabit per second.
Chapter 10: Traffic Management
793
Summary of Contents for NetDefendOS
Page 30: ...Figure 1 3 Packet Flow Schematic Part III Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 30 ...
Page 32: ...Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 32 ...
Page 144: ...Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 144 ...
Page 284: ...Chapter 3 Fundamentals 284 ...
Page 392: ...Chapter 4 Routing 392 ...
Page 419: ... Host 2001 DB8 1 MAC 00 90 12 13 14 15 5 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 419 ...
Page 420: ...Chapter 5 DHCP Services 420 ...
Page 573: ...Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 573 ...
Page 607: ...Chapter 7 Address Translation 607 ...
Page 666: ...Chapter 8 User Authentication 666 ...
Page 775: ...Chapter 9 VPN 775 ...
Page 819: ...Chapter 10 Traffic Management 819 ...
Page 842: ...Chapter 11 High Availability 842 ...
Page 866: ...Default Enabled Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 866 ...
Page 879: ...Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 879 ...