10.1.5. Creating Differentiated Limits Using Chains
In the previous examples a static traffic limit for all outbound connections was applied. What if
the aim is to limit web surfing more than other traffic? Assume that the total bandwidth limit is
250 Kbps and 125 Kbps of that is to be allocated to web surfing inbound traffic.
The Incorrect Solution
Two "surfing" pipes for inbound and outbound traffic could be set up. However, it is not usually
required to limit outbound traffic since most web surfing usually consists of short outbound
server requests followed by long inbound responses.
A surf-in pipe is therefore first created for inbound traffic with a 125 Kbps limit. Next, a new Pipe
Rule is set up for surfing that uses the surf-in pipe and it is placed before the rule that directs
everything else through the std-in pipe. That way web surfing traffic goes through the surf-in
pipe and everything else is handled by the rule and pipe created earlier.
Unfortunately this will not achieve the desired effect, which is allocating a maximum of 125 Kbps
to inbound surfing traffic as part of the 250 Kbps total. Inbound traffic will pass through one of
two pipes: one that allows 250 Kbps, and one that allows 125 Kbps, giving a possible total of 375
Kbps of inbound traffic but this exceeds the real limit of 250 Kbps.
The Correct Solution
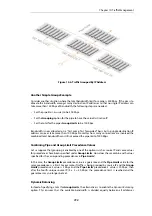
To provide the solution, create a
chain
of the surf-in pipe followed by the std-in pipe in the pipe
rule for surfing traffic. Inbound surfing traffic will now first pass through surf-in and be limited to
a maximum of 125 Kbps. Then, it will pass through the std-in pipe along with other inbound
traffic, which will apply the 250 Kbps total limit.
Figure 10.3. Differentiated Limits Using Chains
If surfing uses the full limit of 125 Kbps, those 125 Kbps will occupy half of the std-in pipe leaving
125 Kbps for the rest of the traffic. If no surfing is taking place then all of the 250 Kbps allowed
through std-in will be available for other traffic.
This does not provide a bandwidth guarantee for web browsing but instead limits it to 125 Kbps
Chapter 10: Traffic Management
783
Summary of Contents for NetDefendOS
Page 30: ...Figure 1 3 Packet Flow Schematic Part III Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 30 ...
Page 32: ...Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 32 ...
Page 144: ...Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 144 ...
Page 284: ...Chapter 3 Fundamentals 284 ...
Page 392: ...Chapter 4 Routing 392 ...
Page 419: ... Host 2001 DB8 1 MAC 00 90 12 13 14 15 5 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 419 ...
Page 420: ...Chapter 5 DHCP Services 420 ...
Page 573: ...Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 573 ...
Page 607: ...Chapter 7 Address Translation 607 ...
Page 666: ...Chapter 8 User Authentication 666 ...
Page 775: ...Chapter 9 VPN 775 ...
Page 819: ...Chapter 10 Traffic Management 819 ...
Page 842: ...Chapter 11 High Availability 842 ...
Page 866: ...Default Enabled Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 866 ...
Page 879: ...Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 879 ...