C. Now, return to the first loopback interface and set the LoopTo property:
gw-world:/> set Interface LoopbackInterface LB1 LoopTo=LB2
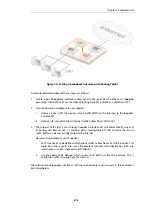
3.4.10. Interface Groups
Any set of NetDefendOS interfaces can be grouped together into an
Interface Group
. This then
acts as a single NetDefendOS configuration object which can be used in creating security policies
in the place of a single group. When a group is used, for example, as the source interface in an IP
rule , any of the interfaces in the group could provide a match for the rule.
A group can consist of ordinary Ethernet interfaces or it could consist of other types such as
VLAN interfaces or VPN Tunnels. Also, the members of a group do not need to be of the same
type. A group might consist, for example, of a combination of two Ethernet interfaces and four
VLAN interfaces.
The Security/Transport Equivalent Option
When creating an interface group, the option
Security/Transport Equivalent
can be enabled (it is
disabled by default). Enabling the option means that the group can be used as the destination
interface in NetDefendOS rules where connections might need to be moved between two
interfaces. For example, the interface might change with route failover or OSPF.
If a connection is moved from one interface to another within a group and
Security/Transport
Equivalent
is enabled, NetDefendOS will not check the connection against the NetDefendOS rule
sets with the new interface.
With the option disabled, a connection cannot be moved to another interface in the group and is
instead dropped and must be reopened. This new connection is then checked against the
NetDefendOS rule sets. In some cases, such as an alternative interface that is much slower, it may
not be sensible to allow certain connections over the new interface.
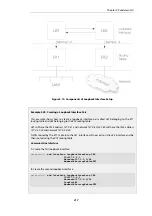
Example 3.26. Creating an Interface Group
Command-Line Interface
gw-world:/> add Interface InterfaceGroup examplegroup
Members=exampleIf1,exampleIf2
Web Interface
1.
Go to: Network > Interfaces and VPN > Interface Groups > Add > InterfaceGroup
2.
Enter the following information to define the group:
•
Name: The name of the group to be used later
•
Security/Transport Equivalent: If enabled, the interface group can be used as a
destination interface in rules where connections might need to be moved between the
Chapter 3: Fundamentals
218
Summary of Contents for NetDefendOS
Page 30: ...Figure 1 3 Packet Flow Schematic Part III Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 30 ...
Page 32: ...Chapter 1 NetDefendOS Overview 32 ...
Page 144: ...Chapter 2 Management and Maintenance 144 ...
Page 284: ...Chapter 3 Fundamentals 284 ...
Page 392: ...Chapter 4 Routing 392 ...
Page 419: ... Host 2001 DB8 1 MAC 00 90 12 13 14 15 5 Click OK Chapter 5 DHCP Services 419 ...
Page 420: ...Chapter 5 DHCP Services 420 ...
Page 573: ...Chapter 6 Security Mechanisms 573 ...
Page 607: ...Chapter 7 Address Translation 607 ...
Page 666: ...Chapter 8 User Authentication 666 ...
Page 775: ...Chapter 9 VPN 775 ...
Page 819: ...Chapter 10 Traffic Management 819 ...
Page 842: ...Chapter 11 High Availability 842 ...
Page 866: ...Default Enabled Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 866 ...
Page 879: ...Chapter 13 Advanced Settings 879 ...