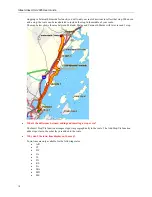
Getting Started with Street Atlas USA 2005
17
Differential GPS (DGPS)
A technique to improve GPS accuracy that uses pseudo-range errors recorded at a known location to improve the
measurements made by other GPS receivers within the same general geographic area.
Dilution of Precision (DOP)
The total effect of all error sources in locating a position.
DOP
Dilution Of Precision
Download
To transfer information from a remote unit, such as a GPS receiver, to a computer.
EDT
Eastern daylight time
Elevation field (GPS)
When GPS tracking, displays your current elevation (due to Selective Availability which can vary as much as 512
feet (156 meters); however, 95 percent of the time you can expect greater accuracy.) Elevation is the height above
sea-level.
Ephemeris
Data which indicates the position and status of satellites.
EST
Eastern standard time
GMT
Greenwich mean time; used as the standard of time throughout the world.
GPS
Global Positioning System; a "constellation" of orbiting satellites used to calculate a precise position on or near the
earth's surface.
HDOP
The measure of how much the geometry of the satellites affects the horizontal position estimate.
Heading
Azimuth of the longitudinal axis of an aircraft or ship. Heading may differ from direction of travel when flying or
boating due to currents in the air or water.
Initialize
To set to a starting position, as in obtaining initial coordinates for a GPS receiver.
Latitude
Position north or south of the equator in degrees, minutes, and seconds.
Log
A record of the speed, direction, and route of travel as obtained via GPS.
Logging
Recording the speed, direction, and route traveled using GPS.
Longitude
Position east or west of the prime meridian in degrees, minutes, and seconds.