Configuring Fast Spanning Tree
Page 17-34
Configuring Fast Spanning Tree
The Fast Spanning Tree (Rapid Reconfiguration) feature is designed to help provide an
802.1D standards-based method of quick recovery in the event of link, port and device
failures in an Ethernet local area network. By automatically identifying and utilizing
alternative secondary links, Fast Spanning Tree can rapidly converge backup connections
between network devices within as little as 1 second. In addition, new Spanning Tree
information can be processed faster.
If packets are broadcast to all ports (or flooded) in an attempt to deliver the data, networks
with physical loops will rebroadcast packets repeatedly and cause a network to become
severely congested. This congestion will adversely affect network performance.
While Spanning Tree prevents broadcast storms by blocking ports in the physical topology
that could result in flooded traffic being looped, Fast Spanning Tree minimizes downtime by
bringing these blocked secondary links into Forwarding mode as quickly as possible. If the
Root Port is lost, an Alternate Port on the Bridge can be made the new Root Port, and placed
into a Forwarding state immediately. The prior Root Port switches to a Listening state if it
becomes a Designated Port; otherwise, it enters a Blocking state.
Similarly, any Designated Port on the Bridge can be made the new Root Port, and placed into
a Forwarding state immediately. In this event, the existing (prior) Root Port changes to a
Designated Port role, without a corresponding gain or loss of connectivity. A Backup Port can
also be made the new Root Port and placed into Forwarding mode, resulting in the
Designated Port assuming a Listening state.
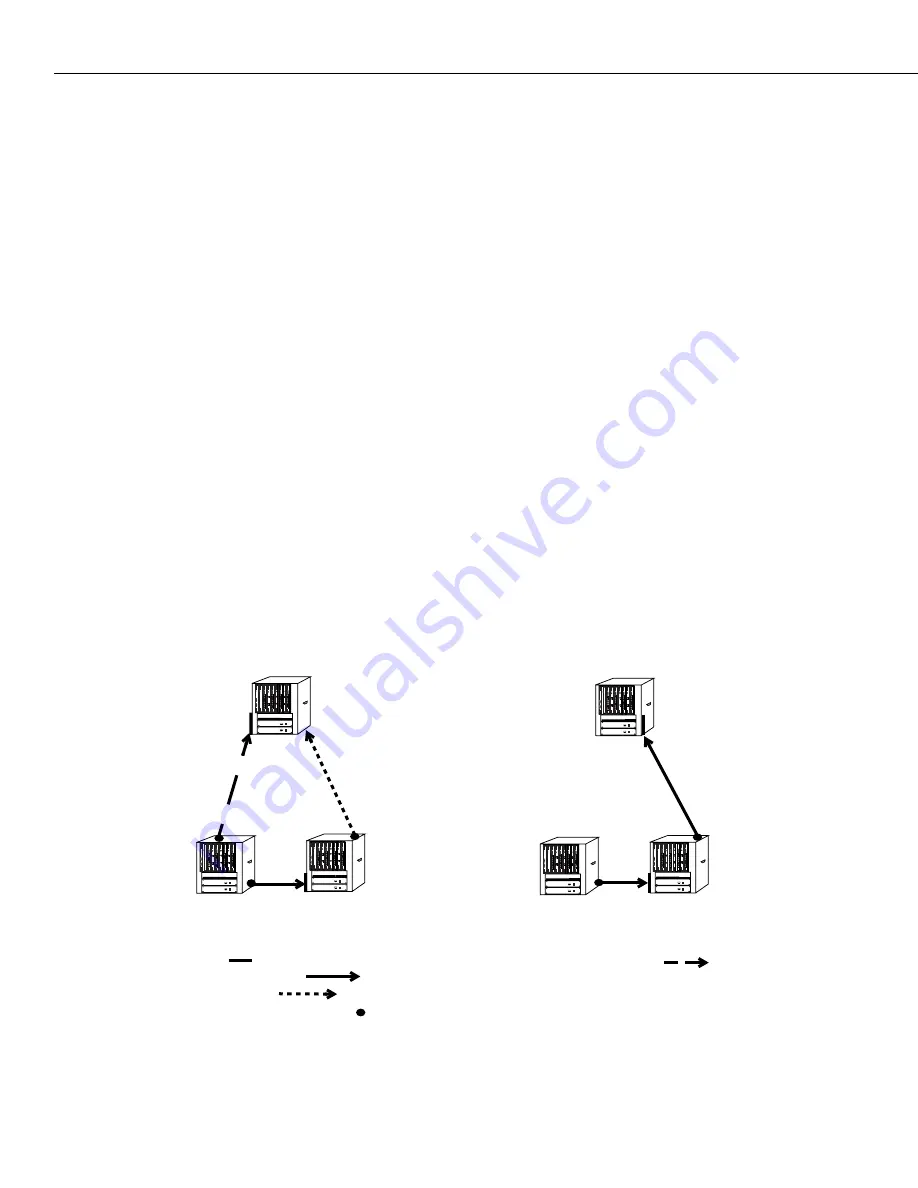
The following diagram illustrates how a typical network connection can fail, such as the A-C
Link shown below. Rapid Reconfiguration brings a blocked link - such as the B-C Link - into
Forwarding state, helping achieve quick recovery from failure of networked devices.
Recovering from Linked Device Failure with Fast Spanning Tree
Bridge C
Bridge B
Bridge A
A-C Link that will Fail =
Designated Bridge for Link =
Spanning Tree Link =
Redundant Link =
Root Port =
Bridge C
Bridge B
Bridge A
B-C becomes Root Port for C
(Backup Root 1)
(Root Bridge)
Содержание Omni Switch/Router
Страница 1: ...Part No 060166 10 Rev C March 2005 Omni Switch Router User Manual Release 4 5 www alcatel com ...
Страница 4: ...page iv ...
Страница 110: ...WAN Modules Page 3 40 ...
Страница 156: ...UI Table Filtering Using Search and Filter Commands Page 4 46 ...
Страница 164: ...Using ZMODEM Page 5 8 ...
Страница 186: ...Displaying and Setting the Swap State Page 6 22 ...
Страница 202: ...Creating a New File System Page 7 16 ...
Страница 270: ...Displaying Secure Access Entries in the MPM Log Page 10 14 ...
Страница 430: ...OmniChannel Page 15 16 ...
Страница 496: ...Configuring Source Route to Transparent Bridging Page 17 48 ...
Страница 542: ...Dissimilar LAN Switching Capabilities Page 18 46 ...
Страница 646: ...Application Example DHCP Policies Page 20 30 ...
Страница 660: ...GMAP Page 21 14 ...
Страница 710: ...Viewing the Virtual Interface of Multicast VLANs Page 23 16 ...
Страница 722: ...Application Example 5 Page 24 12 ...
Страница 788: ...Viewing UDP Relay Statistics Page 26 24 ...
Страница 872: ...The WAN Port Software Menu Page 28 46 ...
Страница 960: ...Deleting a PPP Entity Page 30 22 ...
Страница 978: ...Displaying Link Status Page 31 18 ...
Страница 988: ...Displaying ISDN Configuration Entry Status Page 32 10 ...
Страница 1024: ...Backup Services Commands Page 34 14 ...
Страница 1062: ...Diagnostic Test Cable Schematics Page 36 24 ...
Страница 1072: ...Configuring a Switch with an MPX Page A 10 ...
Страница 1086: ...Page B 14 ...
Страница 1100: ...Page I 14 Index ...
















































