115
1
S
PECIFI
C
A
T
IONS
SPECIFICATIONS
1.6.2
MC on the inverter power supply side
(common)
On the inverter input side, it is recommended to provide an
MC for the following purposes.
1) To release the inverter from the power supply
when the inverter protective function is
activated or the drive becomes faulty (e.g.
emergency stop operation)
When cycle operation or heavy-duty operation is
performed with an optional brake resistor
connected, overheat and burnout of the
discharging resistor can be prevented if a
regenerative brake transistor is damaged due to
insufficient heat capacity of the discharging
resistor and excess regenerative brake duty.
2) To prevent any accident due to an automatic
restart at restoration of power after an inverter
stop made by a power failure
3) To rest the inverter for an extended period of
time
The control power supply for inverter is always
running and consumes a little power. When
stopping the inverter for an extended period of
time, powering OFF the inverter will save power
slightly.
4) To separate the inverter from the power
supply to ensure safety of maintenance/
inspection work
The inverter's input side MC is used for the above
purpose, select class JEM1038-AC3 MC for the
inverter input side current when making an
emergency stop during normal operation.
Since repeated inrush current at powering ON will shorten
the life of the converter circuit (switching life is 1 million
times (about 500,000 times for the 200V class 37K or
more), frequent starts/stops must be avoided.
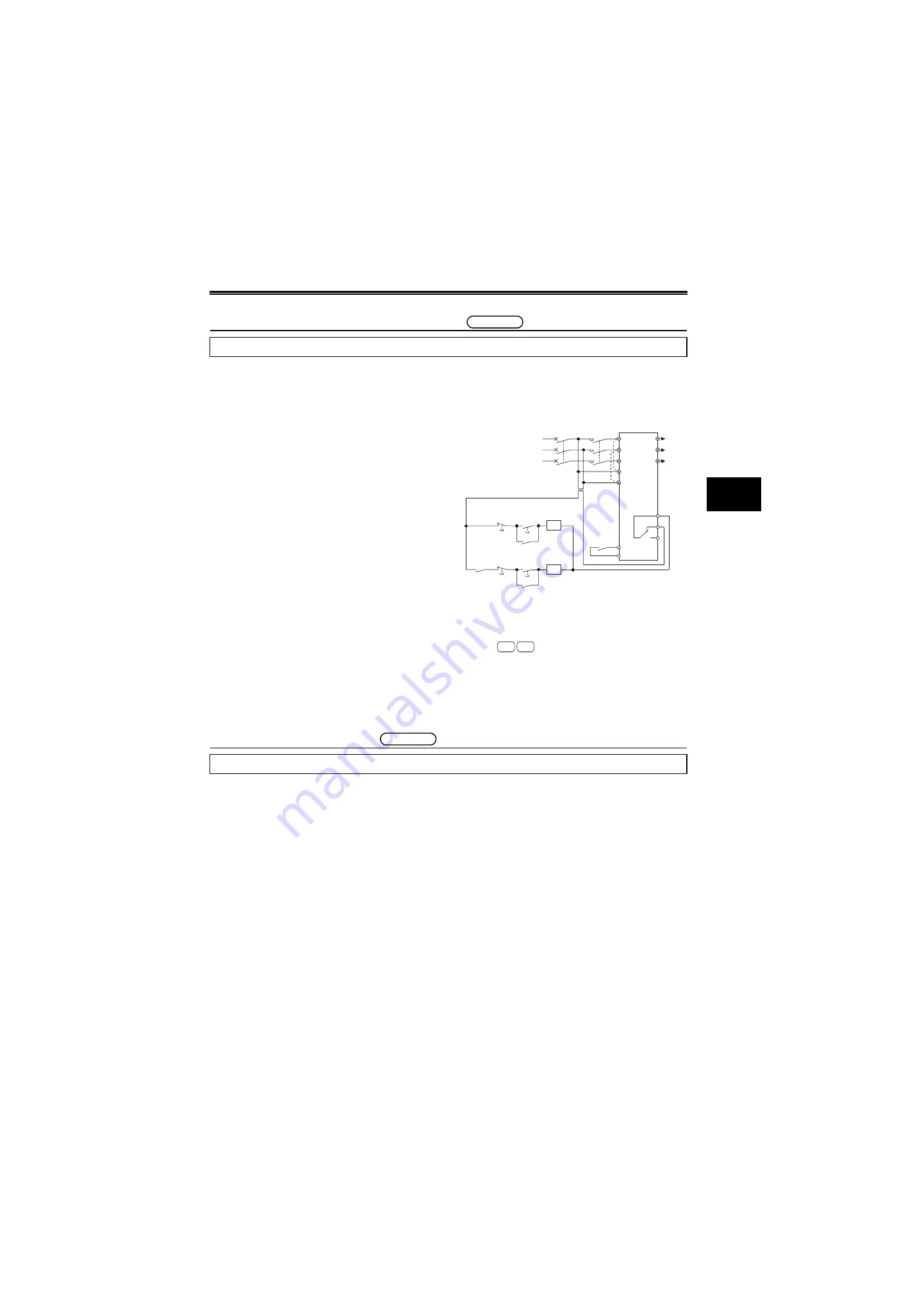
As shown below, always use the start signal (turn ON/OFF
terminals STF, STR-SD) to start/stop the inverter.
*1
When the power supply is 400V class, install a step-
down transformer.
*2
For
, connect the power supply terminals R1/
L11, S1/L21 of the control circuit to the input side of the
MC to hold an fault signal when the inverter's protective
circuit is activated. At this time, remove jumpers across
terminals R/L1 and R1/L11, and across S/L2 and S1/L21.
(Refer to page 36 for removal of the jumper)
1.6.3
Inverter power restart
(common)
When the motor is driven by the inverter, direct-on line
starting is always made at a low frequency to suppress the
motor starting current and the frequency is increased
gradually. Hence, when the coasting motor is started by the
inverter, the inverter attempts to draw the motor frequency
into the starting frequency. However, if the load energy is
large, a large current may flow to the inverter side due to
the power returned from the motor to the inverter, causing
an overcurrent shut-off (E.OC1 to E.OC3). Therefore,
provide a coasting interlock circuit so that the inverter may
only start the motor at a motor stop state. (Refer to page
559)
Since a similar phenomenon will take place when terminal
RES is used during inverter operation, note the design of
the circuit.(Refer to page 56)
However, the fast-response current limit function of the
inverter makes it difficult to trip the inverter if the inverter is
restarted during coasting.
Note that the function of automatic restart after
instantaneous power failure may be used to restart the
inverter while the motor is coasting.
Do not use the inverter power supply side MC to start/stop the inverter.
common
Power
supply
MCCB
RA
U
V
A1
B1
C1
W
To the
motor
Inverter
MC
STF(STR)
R/L1
S/L2
T/L3
R1/L11
S1/L21
OFF
ON
MC
Stop
Operation
RA
MC
Operation preparation
Inverter's Start/Stop Circuit Example
Start/Stop
RA
MC
SD
T
*1
*2
A700 F700
The inverter may trip if it is restarted while the motor is coasting.
common
Summary of Contents for FR-A700 Series
Page 245: ...279 2 PARAMETER PARAMETER MEMO ...
Page 440: ...474 PARAMETER MEMO ...
Page 522: ...556 SELECTION MEMO ...