2-18
ALPS Advanced Line Protection System
GE Power Management
2.3 PROTECTION SETTINGS
2 CALCULATION OF SETTINGS
2
309: Z3GRDCHAR - Zone 3 Ground Characteristic (Revision B models only)
Z3GRDCHAR can be set to MHO or QUAD. This setting determines the measuring unit used for the Zone 3 ground dis-
tance functions. The distance function may be set as an Mho (MHO) or as a quadrilateral (QUAD).
310: Z3RGREACH - Zone 3 Resistive Ground Reach (Revision B models only)
Z3RGREACH can be set from 0.01 to 100.00
Ω
for a 5 A rated relay (0.05 to 500
Ω
for a 1 A rated relay). It determines the
position of the right resistive blinder for the ground distance quadrilateral characteristic to provide coverage for resistive
ground faults. If Zone 4 is also set to Quad mode looking forward, this setting should be calculated at 0.8 or less of the
Zone 4 Resistive Ground Reach (Protection Setting 413: Z4RGREACH). If Zone 3 is not set to Quad mode, the setting
should be calculated as 0.8 (if “tent” characteristics are used) or less (0.6 to 0.7 if “tent” characteristics are not used) of the
positive-sequence resistance seen by the relay under maximum load conditions and unity power factor. Also, to maintain
zone accuracy, it is recommended that the resistive reach is not greater than 10 times the Ground Distance Reach (Protec-
tion Setting 305: Z3GRDREACH) for this zone.
2.3.5 Z4DISTANCE
The settings to be used on the Zone 4 distance functions in the ALPS system depend on the application and the scheme
selected. Both the phase and ground distance functions can be set to look in the reverse direction relative to the Zone 1,
Zone 2 and Zone 3 phase and ground distance functions (see below). The reverse direction is required in certain applica-
tions and/or schemes as described below.
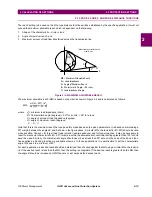
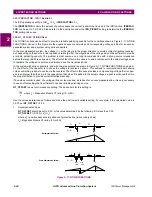
Figure 2–8: GROUND DISTANCE FUNCTION CHARACTERISTIC
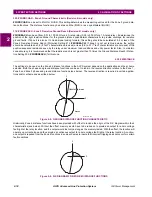
Historically, Zone 4 distance functions have been provided with offset to include the origin of the R-X diagram within their
characteristics (see below). Without the offset, memory would have to be relied on to provide an output for a zero voltage
fault right at the relay location, and the output would last only as long as the memory lasted. With the offset, the function will
operate on current alone and thus provide a continuous output for a zero voltage fault right at the relay location. A continu-
ous output is required from the Zone 4 functions in some schemes to insure that incorrect tripping does not occur for certain
fault conditions.
Figure 2–9: R-X DIAGRAM FOR ZONE 4 DISTANCE FUNCTIONS
Z4PHREACH
Zr
X
R
Forward
Reverse
Z4PHREACH.CDR
Zr
X
R
OFFSET