GE Power Management
ALPS Advanced Line Protection System
2-29
2 CALCULATION OF SETTINGS
2.3 PROTECTION SETTINGS
2
712: V1COMPTDPU - V1COMP Function Time Delayed Pickup
V1COMPTDPU establishes the pickup setting of the time delayed V1COMP function and can be set from 1.0 to 1.4 per unit
volts based on the RATEDVOLTS setting. If V1COMP is selected, make a V1COMPTDPU setting that is suitable to the
particular application.
713: V1COMPTDLY - V1COMP Overvoltage Function Time Delay
V1COMPTDLY establishes the time delay to be used with the time delayed positive sequence overvoltage function and can
be set from 0 to 10.0 seconds. If V1COMP is selected, make a V1COMPTDLY setting that is suitable to the particular appli-
cation.
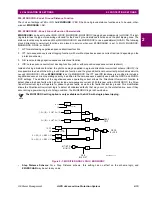
714: FUSEFAIL - Potential Fuse Failure Blocking
Since a distance or directional function may operate for a full or partial loss of AC potential caused by one or more blown
fuses, FUSEFAIL is provided to block distance and directional function tripping when a fuse failure is detected. If the
backup overcurrent functions 50, 50G, and 51G are non-directional they will be allowed to trip. If 50, 50G or 51G are direc-
tional, then they will not be allowed to trip. Figure 1–3: POTENTIAL FUSE FAILURE LOGIC DIAGRAMS on page 1–11
shows the functional logic for the FUSEFAIL function.
If AC potential is lost, the positive-sequence voltage detector V1 drops out, NOT1 produces a logic 1 output to the upper
input of AND1. The V1 pickup setting is fixed at 75% of RATEDVOLTS. The middle input to AND1 is present if load current
is sufficient to operate the current detector IB, while the bottom input is dependent upon whether the fault detector has
operated or one or more poles of the breaker are open. When the POLE DISAGREEMENT logic detects that one or more
poles of the circuit breaker(s) are open, FUSEFAIL is disabled.
If AC potential is lost for any reason, including a blown fuse or fuses, and there is no disturbance on the power system so
that the fault detector has not operated, AND1 produces an output that times-out TL1 and produces a FUSEFAIL output via
OR2. The output of OR2 is routed to AND2 to seal in the FUSEFAIL output, based on the output of V1, so that FUSEFAIL
output is maintained as long as the potential is below normal. When the potential returns to normal, V1 and NOT1 reset to
remove the seal-in, allowing the FUSEFAIL output to reset.
When a fault occurs, with an attendant drop in potential, the V1 function resets, but the fault detector operates to prevent an
output from AND1. FUSEFAIL does not operate on fault conditions.
FUSEFAIL can be set to NO or YES. If BLOCK is selected, then an output will be prevented from any function that requires
potential to operate (distance, directional and any directionally controlled function). If NO is selected, nothing will be
blocked in the event a potential failure occurs.
2.3.10 BLK RECLOS
The following Protection Settings (801 to 810) determine which functions or logic outputs are used to block the Reclose Ini-
tiate (RI) output and to operate the Reclose Cancel (RC) output. Each of the settings may be set to YES or NO to select or
not select the function/logic output respectively.
801: ALL_BELOW - Block Reclosing for all Selectable Functions
Setting ALL_BELOW to YES will block reclosing and energize the reclose cancel contacts for all of the functions controlled
by Settings 802 through 810.
802: OUTOFSTEP - Block For Out Of Step
Set OUTOFSTEP = YES if reclosing is to blocked for a trip resulting during an out of step condition.
803: ALL_3_Z2PH - Block For Three Phase Faults
Set ALL_3_Z2PH = YES if reclosing is to be blocked for all three-phase faults as indicated by the operation of all three (AB,
BC and CA) of the Zone 2 phase distance functions.
804: 50G_BLOCK - Block For 50G
Set 50G_BLOCK = YES if reclosing is to be blocked following a trip initiated by the 50G ground overcurrent function.