⎯
154
⎯
6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6
3.1.6 Fault Detector Module
Models 400 and 500 series have an independent fault detector in the form of a check relay, and
provide the highest order of security against non-power system fault tripping.
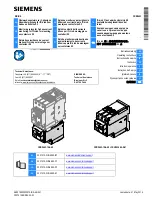
As shown in Figure 3.1.6.1, the fault detector module consists of an analog filter, multiplexer,
analog to digital (A/D) converter, main processing unit (MPU) and output auxiliary relays. The
entire processing from filtering to operation for the measuring elements and output control is
carried out within this module.
The fault detector module receives 3 voltage (Va, Vb, Vc) inputs and 4 current (Ia, Ib, Ic, 3I0)
inputs. The analog filter carries out low-pass filtering for the corresponding current and voltage
signals.
The A/D converter has a resolution of 12 bits and samples input signals at sampling frequencies of
2400 Hz (at 50 Hz) and 2880 Hz (at 60 Hz).
The MPU implements 60 MIPS and uses a RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) type 32-bit
microprocessor. Once the fault detector measuring elements start operating, the high-speed
auxiliary relays FD1 and FD2 operate.
The fault detector module incorporates 8 binary output auxiliary relays (BO1-BO8) each with one
normally open contact.
Fault detector module
Figure 3.1.6.1 Fault Detector Module
Auxiliary relay
Analog filter
Multiplexer
A/D
converter
MPU
Analog filter
Analog filter
FD1
Auxiliary relay
(high speed)
FD2
BO1
BO8
Analog
input
Tripping
command
Binary
output
signals
Summary of Contents for GRZ100 B Series
Page 264: ... 263 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix A Block Diagram ...
Page 271: ... 270 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 ...
Page 272: ... 271 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix B Signal List ...
Page 307: ... 306 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 ...
Page 308: ... 307 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix C Variable Timer List ...
Page 310: ... 309 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix D Binary Input Output Default Setting List ...
Page 321: ... 320 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 ...
Page 322: ... 321 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix E Details of Relay Menu and LCD Button Operation ...
Page 331: ... 330 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 ...
Page 340: ... 339 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix G Typical External Connections ...
Page 377: ... 376 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 ...
Page 384: ... 383 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix J Return Repair Form ...
Page 388: ... 387 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Customer Name Company Name Address Telephone No Facsimile No Signature ...
Page 389: ... 388 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 ...
Page 390: ... 389 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix K Technical Data ...
Page 401: ... 400 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 ...
Page 402: ... 401 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix L Symbols Used in Scheme Logic ...
Page 405: ... 404 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 ...
Page 406: ... 405 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix M Example of Setting Calculation ...
Page 417: ... 416 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 ...
Page 418: ... 417 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix N IEC60870 5 103 Interoperability and Troubleshooting ...
Page 434: ... 433 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix P Inverse Time Characteristics ...
Page 437: ... 436 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 ...
Page 438: ... 437 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix Q Failed Module Tracing and Replacement ...
Page 444: ... 443 6 F 2 S 0 8 4 6 Appendix R Ordering ...
Page 447: ......