Text Editing on the Graph
372 User Manual
3Ć103
ăStep 1:ă
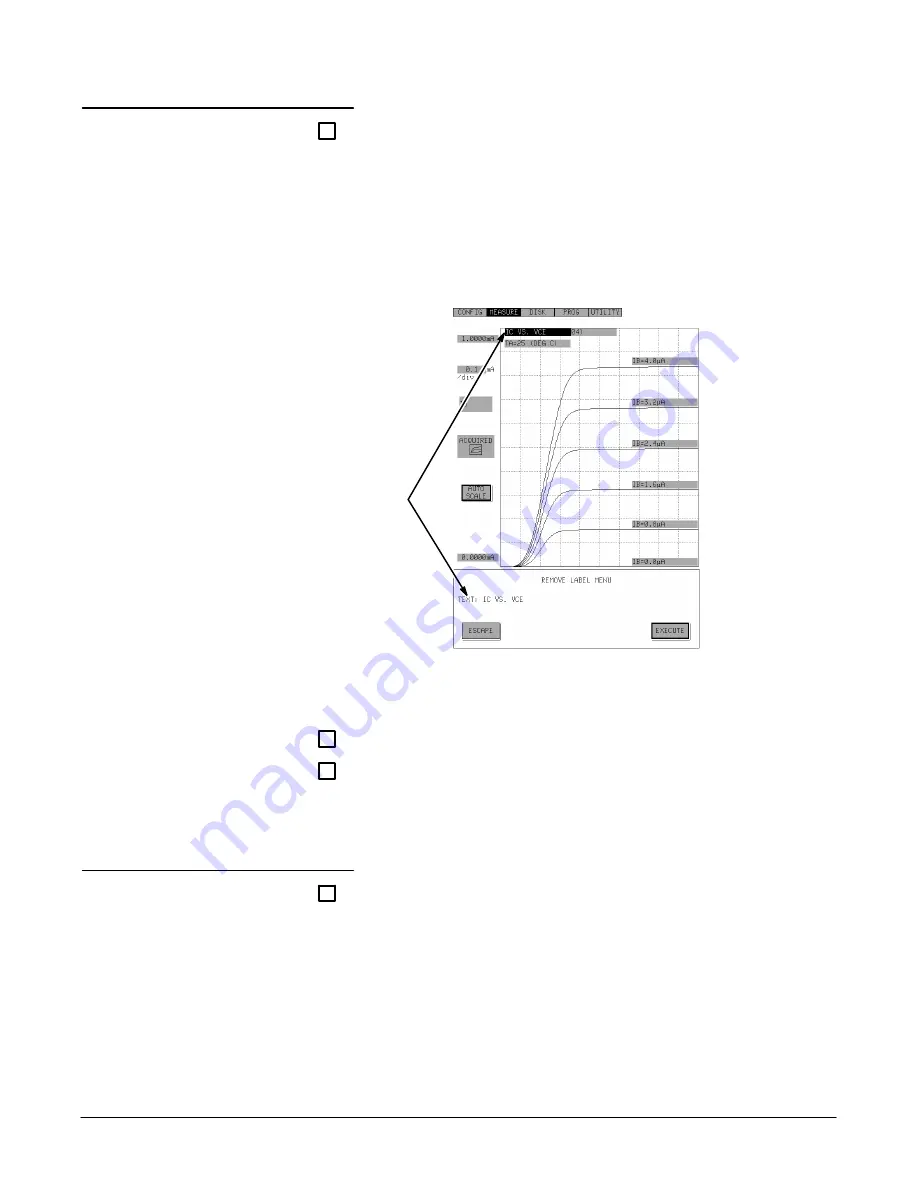
Touch the [REMOVE LABEL] soft button to bring up the Move
Label popĆup menu (see Figure 3Ć44).
When more than one label exists, all labels are changed to the selectorĆ
formed labels. First select the label, then removed it.
When there is only one label, the label is already highlighted to indicate
that it can be removed. In this case, skip step 2 and go on to step 3.
Text Selected
Figure 3Ć44:ăRemove Label PopĆup Menu
ăStep 2:ă
Select the label to be removed by touching it
ăStep 3:ă
Touch the [EXECUTE] soft button to set the label. To cancel,
touch the [ESCAPE] soft button. Touching either soft button causes the
Remove Label popĆup menu to disappear.
ăStep 1:ă
Touch the [RENAME LABEL] soft button to bring up the Move
Label popĆup menu (see Figure 3Ć45).
When there is more than one label on the graph, all labels are changed
to the selectorĆformed labels. First select the label and then rename it.
When there is only one label, the label is enclosed with a line to indiĆ
cates that it can be renamed. In this case, skip step 2 and go on to
step 3.
Removing the Label
Renaming the Label
Summary of Contents for 372
Page 4: ......
Page 6: ...About this Manual ii ...
Page 14: ...Contents x ...
Page 22: ...Contents xviii ...
Page 30: ...Consignes de Sécurité Safety Summary xxvi ...
Page 31: ...Getting Started ...
Page 32: ......
Page 36: ...Overview Getting Started 1Ć4 ...
Page 90: ...Tutorial Ć About the Sample Disk Getting Started 1Ć58 ...
Page 91: ...Operating Basics ...
Page 92: ......
Page 108: ...Mounting the Device Under Test Operating Basics 2Ć16 ...
Page 110: ...Before and After Floating Measurement Operating Basics 2Ć18 ...
Page 111: ...Reference ...
Page 112: ......
Page 174: ...Pulse Mode Reference 3Ć62 ...
Page 176: ...Auxiliary Voltage Supply Reference 3Ć64 ...
Page 186: ...Adjusting the Graph Display Reference 3Ć74 ...
Page 190: ...Mathematical Operation Reference 3Ć78 ...
Page 210: ...Zoom Reference 3Ć98 ...
Page 217: ...Text Editing on the Graph 372 User Manual 3Ć105 Figure 3Ć46 ăClear Labels PopĆup Menu ...
Page 218: ...Text Editing on the Graph Reference 3Ć106 ...
Page 228: ...Hardcopy Reference 3Ć116 ...
Page 230: ...Initializing the 372 Reference 3Ć118 ...
Page 234: ...Time Stamp Reference 3Ć122 ...
Page 236: ...Adjusting CRT Brightness Reference 3Ć124 ...
Page 238: ...ID Information Reference 3Ć126 ...
Page 254: ...Floppy Disk System Reference 3Ć142 ...
Page 280: ...Sample Programs Reference 3Ć168 ...
Page 286: ...GPIB Reference 3Ć174 ...
Page 287: ...Appendices ...
Page 288: ......
Page 292: ...Appendix B Specifications Appendices AĆ4 ...
Page 312: ...Appendix B Specifications Appendices AĆ24 ...
Page 358: ...Appendix B Specifications Appendices AĆ70 ...






























