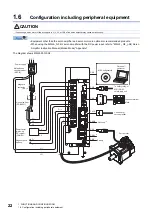
18
1 FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION
1.3 Outline of CC-Link IE Field Network Basic
1.3
Outline of CC-Link IE Field Network Basic
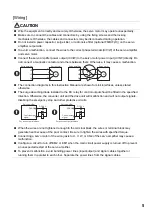
CC-Link IE Field Network Basic is a standard Ethernet-based protocol used to perform cyclic communication by the installed
software without using a dedicated ASIC. You can establish a highly flexible system because CC-Link IE Field Network Basic
can be used together with TCP/IP communications.
Up to 64 servo amplifiers (up to 16 servo amplifiers per group) can be monitored by the controller.
In the point table mode (pt), you can perform positioning operation by specifying the pre-configured point table number (1 to
255) with a controller.
Feature
• High-speed communication
High-speed communication can be established by cyclic transmission of not only bit data but also word data.
The maximum communication speed is 100 Mbps.
• General-purpose Ethernet supported
Dedicated control wiring is unnecessary, and a single Ethernet network can be established.
1.4
Function list
The following table lists the functions of this servo. For details of the functions, refer to each section indicated in the detailed
explanation field. "MR-J4-_GF_" means "MR-J4-_GF_(-RJ) Servo Amplifier Instruction Manual (Motion Mode)".
Function
Description
Detailed
explanation
Model adaptive control
This function achieves a high response and stable control following the ideal model. The two-degrees-
of-freedom model adaptive control enables you to set a response to the command and a response to
the disturbance separately. This function can be disabled. To disable this function, refer to section 7.5 of
"MR-J4-_GF_(-RJ) Servo Amplifier Instruction Manual (Motion Mode)".
Homing mode (hm)
The servo amplifier operates in the home position return mode.
Jog mode (jg)
This is a control mode where the servo motor speed is set to drive the servo motor manually in the
commutation with a controller. This control mode is not in CiA 402 standard (Mitsubishi Electric original).
Point table mode (pt)
This is a control mode where the servo motor is driven according to the commands of the travel
distance, speed and others stored in the specified point table No. in the commutation with a controller.
This control mode is not in CiA 402 standard (Mitsubishi Electric original).
Indexer mode (idx)
In this control mode, the servo motor is driven to the station specified in the communication with a
controller. This control mode is not in CiA 402 standard (Mitsubishi Electric original).
Roll feed display
function
Positions based on specified travel distance from a status display "0" of current/command positions at
start.
This is available with servo amplifiers with software version A7 or later.
Touch probe function
setting
When the touch probe signal turns on, the current position is latched. The latched data can be read with
communication commands.
High-resolution encoder
Rotary servo motors compatible with the MELSERVO-J4 series are equipped with a high-resolution
encoder of 4194304 pulses/rev.
Absolute position
detection system
Home position return is required only once, and not required at every power-on.
MR-J4-_GF_ chapter 12
Gain switching function
You can switch gains during rotation/stop, and can use input devices to switch gains during operation.
MR-J4-_GF_ section 7.2
Advanced vibration
suppression control II
This function suppresses vibration and residual vibration at an arm end.
MR-J4-_GF_ section 7.1
Machine resonance
suppression filter
This filter function (notch filter) decreases the gain of the specific frequency to suppress the resonance
of the mechanical system.
MR-J4-_GF_ section 7.1
Shaft resonance
suppression filter
When a load is mounted to the servo motor shaft, resonance by shaft torsion during driving may
generate a mechanical vibration at high frequency. The shaft resonance suppression filter suppresses
the vibration.
MR-J4-_GF_ section 7.1
Adaptive filter II
The servo amplifier detects mechanical resonance and sets filter characteristics automatically to
suppress mechanical vibration.
MR-J4-_GF_ section 7.1
Low-pass filter
Suppresses high-frequency resonance which occurs as the servo system response is increased.
MR-J4-_GF_ section 7.1