EXPERT Standard Series User Manual
153
6.8 Group F7 advanced function parameters
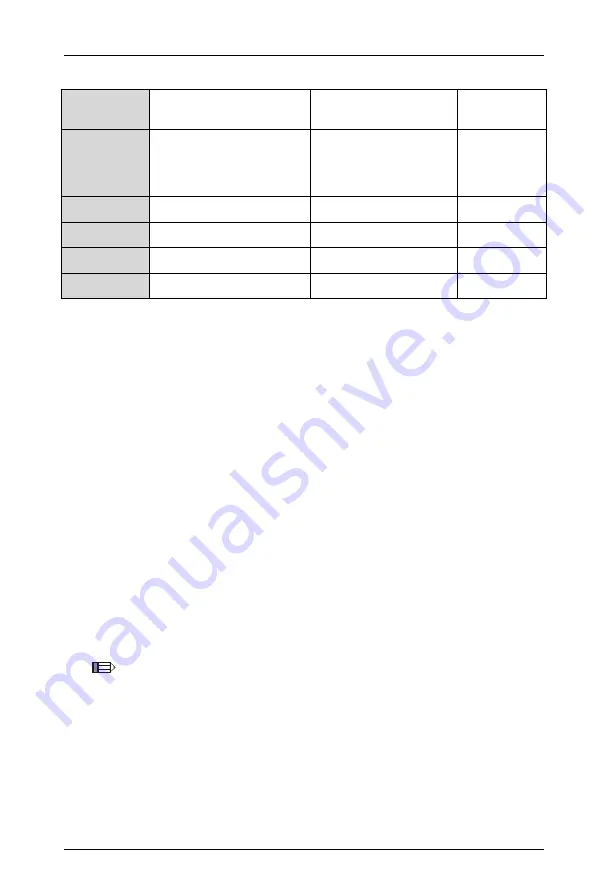
F7.00
Overpressure stall point
110.0~150.0
Model
determination
F7.01
Overvoltage control
voltage
0.000~9.999V (when it
is equal to 0, the
overpressure stall 2 will
not work)
0.000V
F7.02
Overvoltage stall gain Kp1
0~2.00
0.20
F7.03
Overvoltage stall integral
time Ki1
0~2.00
0.20
F7.04
Overvoltage stall gain Kp2
0.0~2.00
0.40
F7.05
Overvoltage stall integral
time Ki2
0~2.00
0.20
During the deceleration of drive, due to the influence of load inertia, the actual decline
rate of motor speed may be lower than that of the output frequency. In this case, the motor
will feed back electric energy to the drive, causing the DC bus voltage of the drive to rise. If
no measures are taken, overvoltage trip will occur.
The overvoltage stall protection function detects the bus voltage during the
deceleration of the drive, and compares it with the stall overvoltage point defined by F7.00
(relative to the standard bus voltage). If it exceeds the stall overvoltage point, the output
frequency of the drive will stop falling, when the bus voltage is detected to be lower than
the stall overvoltage point again, implement deceleration.
Overvoltage stall gain is used to adjust the drive's ability to suppress overvoltage
during deceleration. The larger this value, the stronger the ability to suppress overvoltage.
Under the premise of no overvoltage, the smaller the set value of the gain, the better.
For loads with small inertia, the overvoltage stall gain shall be small, otherwise it will
cause the dynamic response of the system to slow down. For loads with large inertia, this
value shall be large, otherwise the suppression effect will be poor, and the overvoltage fault
may occur.
When the overvoltage stall gain is set to 0, the overvoltage stall function is canceled.
Note:
1. When the set stall point is low, it is suggested that the user shall increase the
deceleration time appropriately.
















































