UMSITRPDS3-1
Installation
November 2010
4-17
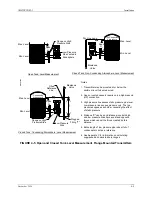
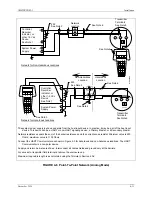
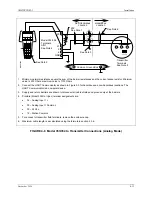
4.3.5.2 Multi-Drop Network
Perform the following simple calculations to ensure that the power supply output voltage permits the
Transmitter to remain within its operating range.
1.
Calculate the minimum power supply output voltage.
Minimum network power supply voltage is a function of Network Resistance and the total current
draw of all transmitters in the network, and is calculated by the following formula:
Minimum Supply Output Voltage = 10.5 volts + [(0.004 × number of transmitters on Network) × (Network Resistance)]
Power supply output voltage must be greater than the calculated value. The minimum voltage across
the input terminals of a transmitter is 10 volts.
2.
Calculate the maximum power supply output voltage.
Maximum network power supply voltage is a function of Network Resistance and total current draw
of all the transmitters in the network, and is calculated by the following formula:
Maximum Supply Output Voltage = V
max
+ [(0.004 × number of transmitters on Network) x (Network Resistance)]
Power supply output voltage must be less than the calculated value. The maximum voltage (
V
max
)
permitted across the input terminals of a transmitter is:
•
Non-intrinsically safe transmitter: 45 volts
•
Intrinsically safe transmitter: 30 volts
The maximum number of transmitters that can be connected to a Multi-Drop Network is 15. Each
transmitter is “parked” in a low current draw mode (4 mA) to conserve power. Ensure that the network
power supply is capable of sourcing the total current consumed by the number of transmitters on the
network.
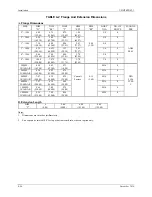
4.3.6 Determining Network (Loop) Length
A cable length calculation is necessary when HART communication is to be employed. Cable capacitance
directly affects maximum network length.
4.3.6.1 Cable Capacitance
Cable type, conductor size, and recommended cable model numbers are stated in Section 9.5.1 Two-Wire
Cable.
Cable capacitance is a parameter used in the calculation of the maximum length of cable that can be used
to construct the network. The lower the cable capacitance the longer the network can be. Manufacturers
typically list two capacitance values for an instrumentation cable:
1.
Capacitance between the two conductors.
2.
Capacitance between one conductor and the other conductor(s) connected to shield. This capacitance
is the worst case value and is to be used in the cable length formula.
Содержание 7MF4033 series
Страница 48: ...Model 275 Universal Hart Communicator UMSITRPDS3 1 November 2010 2 26 ...
Страница 86: ...Installation UMSITRPDS3 1 November 2010 4 34 ...
Страница 152: ...Calibration and Maintenance UMSITRPSD3 1 November 2010 7 20 ...
Страница 158: ...Circuit Description UMSITRPDS3 1 November 2010 8 6 ...
Страница 197: ......
Страница 198: ......
Страница 200: ...Model Designations and Specifications UMSITRPDS3 1 November 2010 9 42 ...
Страница 204: ...Glossary UMSITRPDS3 1 November 2010 10 4 ...
Страница 208: ...Appendix A Online Configuration Map UMSITRPDS3 1 11 4 November 2010 ...
Страница 210: ...Appendix B Hazardous Area Installation UMSITRPDS3 1 12 2 November 2010 FIGURE 12 1 Control Drawing ...
Страница 211: ...UMSITRPDS3 1 Appendix B Hazardous Area Installation November 2010 12 3 FIGURE 12 2 Control Drawing ...
Страница 212: ...Appendix B Hazardous Area Installation UMSITRPDS3 1 12 4 November 2010 FIGURE 12 3 Control Drawing ...
Страница 216: ...Appendix C Elevation and Suppression Correction UMSITRPDS3 1 13 4 November 2010 ...