Teledyne Continental Motors, Inc.
TM
Maintenance
Inspections
7-3.8.2.5. Static and Dynamic Seal Check
Procedure
1.
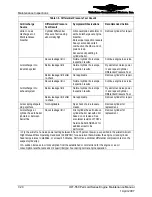
The piston and piston rings form a dynamic seal (Figure 7-6) in the cylinder. Leakage
in this dynamic seal can vary from cylinder to cylinder, based on ring gap position,
wear or the amount of engine oil on the cylinder wall. Note any leakage source (air
discharge) and determine serviceability.
Static Seal
Dynamic Seal
Figure 7-6.
Static and Dynamic Seals on the Engine Cylinder
2.
To check the integrity of the static seals:
a.
Check the seal in the engine cylinder for leakage by listening for air flow at the
Exhaust or Induction System port. If air flow is audible, the static seal is leaking.
b.
If leakage is present around the intake or exhaust valve, stake the valves as
follows:
1)
Remove the rocker covers from the applicable cylinder(s).
2)
Inspect the valve springs, valve retainers, and valve stem for wear.
WARNING
Do not stand or allow anyone to stand in the arc of the
propeller.
3)
Rotate the crankshaft so the piston will not be at top dead center to prevent the
valve from striking the top of the piston in some engines.
4)
Place a fiber drift on the rocker arm directly over the valve stem.
CAUTION: Do not allow the fiber drift to contact the valve spring
retainer or rotocoil.
IOF-550 Permold Series Engine Maintenance Manual
7-21
1 April 2007