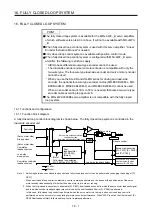
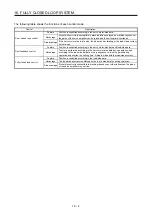
15. USING A DIRECT DRIVE MOTOR
15 - 18
15.4.2 Power supply capacity and generated loss
Calculate the generated loss and the power supply capacity of the servo amplifier under rated load from (1)
and (2) in this section. The calculated value will vary depending on the number of connected direct drive
motors and the capacities of the direct drive motors. For thermal design of an enclosed type cabinet, use the
values calculated in consideration for the worst operating conditions. The actual amount of generated heat
will be intermediate between values at rated torque and servo-off according to the duty used during
operation. When the direct drive motor is run at less than the rated speed, the power supply capacity will be
smaller than the calculated value, but the servo amplifier's generated heat will not change.
(1) Calculation method of power supply capacity
Calculate the power supply capacity for one servo amplifier from tables 15.1 and 15.2.
Table 15.1 Power supply capacity for
one servo amplifier at rated output
Table 15.2 Servo amplifier power
supply capacity for one direct drive
motor
Servo amplifier
(Note)
Power supply capacity
[kVA]
Servo motor
Power supply capacity
[kVA]
(A)
MR-J4W2-22B
Total power supply
capacity of connected
direct drive motors ((A)
in table 15.2)
TM-RFM002C20
0.25
MR-J4W2-44B
TM-RFM004C20
0.38
MR-J4W2-77B
TM-RFM006C20
0.53
MR-J4W2-1010B
TM-RFM006E20
0.46
MR-J4W3-222B
TM-RFM012E20
0.81
MR-J4W3-444B
TM-RFM018E20
1.3
Note.
Note that the power supply capacity will
vary according to the power supply
impedance. This value is applicable when
the power factor improving reactor is not
used.
TM-RFM012G20
0.71
TM-RFM040J10
1.2
Calculate the power supply capacity with equation 10.1 in (1) in section 10.2.
(2) Calculation method of the amount of heat generated by the servo amplifier
Calculate the amount of heat generated by one servo amplifier from tables 15.3 and 15.4.
Table 15.3 Amount of heat generated by one servo amplifier at
rated output
Table 15.4 Amount of heat generated
by one servo amplifier for one direct
drive motor
Servo amplifier
(Note)
Servo amplifier-generated heat [W]
Servo motor
Servo amplifier-
generated heat [W]
(B)
With servo-off (C)
At rated output
MR-J4W2-22B
20
Sum of the total amount of
heat generated by the servo
amplifier for each direct drive
motor ((B) in table 15.4) and
the amount of heat generated
by the servo amplifier with
servo-off (C)
TM-RFM002C20
25
MR-J4W2-44B 20
TM-RFM004C20 35
MR-J4W2-77B 20
TM-RFM006C20 40
MR-J4W2-1010B 20
TM-RFM006E20 40
MR-J4W3-222B 20
TM-RFM012E20 50
MR-J4W3-444B 25
TM-RFM018E20 50
Note.
Heat generated during regeneration is not included in the servo amplifier-
generated heat. To calculate heat generated by the regenerative option,
refer to section 11.2.
TM-RFM012G20
50
TM-RFM040J10
50
Calculate the amount of heat generated by the servo amplifier with equation 10.2 in (2) in section 10.2.
Summary of Contents for MR-J4W2
Page 9: ...A 8 MEMO ...
Page 17: ...8 MEMO ...
Page 31: ...1 FUNCTIONS AND CONFIGURATION 1 14 MEMO ...
Page 95: ...4 STARTUP 4 20 MEMO ...
Page 169: ...6 NORMAL GAIN ADJUSTMENT 6 20 MEMO ...
Page 201: ...7 SPECIAL ADJUSTMENT FUNCTIONS 7 32 MEMO ...
Page 213: ...8 TROUBLESHOOTING 8 12 MEMO ...
Page 219: ...9 OUTLINE DRAWINGS 9 6 MEMO ...
Page 229: ...10 CHARACTERISTICS 10 10 MEMO ...
Page 295: ...13 USING STO FUNCTION 13 14 MEMO ...
Page 327: ...14 USING A LINEAR SERVO MOTOR 14 32 MEMO ...
Page 371: ...16 FULLY CLOSED LOOP SYSTEM 16 24 MEMO ...
Page 521: ...APPENDIX App 38 ...
Page 537: ...MEMO ...
Page 541: ......