Functions
6-132
7SA522 Manual
C53000-G1176-C119-2
6.9
Overcurrent Protection
General
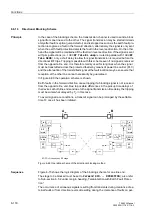
Overcurrent protection is integrated in the 7SA522 device. This function may option-
ally be used either as back-up time delayed overcurrent protection or as emergency
overcurrent protection.
Whereas the distance protection can only function correctly if the measured voltage
signals are available to the device, the emergency overcurrent protection only requires
the currents. The emergency overcurrent function is automatically activated when the
measured voltage signal is lost, e.g. due to a short circuit or interruption of the voltage
transformer secondary circuits (emergency operation). The emergency operation
therefore replaces the distance protection as short circuit protection if loss of the
measured voltage signal is recognized by one of the following conditions:
•
Pick-up of the internal measured voltage monitoring („Fuse–Failure–Monitor“, refer
to Sub-section 6.16.1.3) or
•
if the signal “
” is received via binary
input, indicating that the measured voltage signal is lost.
If one of these conditions arise, the distance protection is immediately blocked and the
emergency operation is activated.
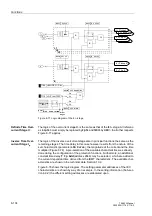
If the overcurrent protection is configured as back-up overcurrent protection it func-
tions independently of the other protective and monitoring functions, therefore also in-
dependent of the distance protection. The back-up overcurrent protection could for in-
stance be used as the only short-circuit protection if the voltage transformers are not
yet available when the feeder is initially commissioned.
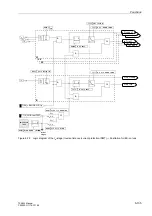
For the overcurrent protection there are in total four stages for the phase currents and
four stages for the earth currents as follows:
•
two overcurrent stages with a definite time characteristic (O/C with DT),
•
one overcurrent stage with inverse time characteristic (IDMT),
•
one further overcurrent stage which is preferably used as a stub protection, but
which can be applied as an additional normal definite time delayed stage.
These four stages are independent of each other and are freely combinable. Blocking
by external criteria via binary input is possible as well as rapid (non delayed) tripping
(e.g. by an external automatic reclose device). During energization of the protected
feeder onto a dead fault it is also possible to release any stage, or also several, for
non-delayed tripping. If not all the stages are required, each individual stage may be
deactivated by setting the pick-up threshold to
∞
.
Summary of Contents for siprotec 7SA522
Page 20: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 64: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 89: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Page 408: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 456: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 516: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 620: ...Appendix B 48 ...