Functions
6-33
7SA522 Manual
C53000-G1176-C119-2
6.2.2
Calculation of the Impedances
6.2.2.1
Method of Operation
A separate measuring system is provided for each of the six possible impedance loops
L1–E, L2–E, L3–E, L1–L2, L2–L3, L3–L1. The phase-earth loops are evaluated when
an earth fault detection according to section 6.2.1 is recognized and the phase current
exceeds a settable minimum value
(address
). The phase-
phase loops are evaluated when the phase current in both of the affected phases ex-
ceeds the minimum value
A jump detector synchronizes all the calculations with the fault inception. If a further
fault occurs during the evaluation, the new measured values are immediately used for
the calculation. The fault evaluation is therefore always done with the measured val-
ues of the current fault condition.
Phase–Phase
Loops
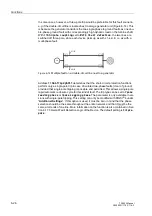
To calculate the phase-phase loop, for instance during a two-phase short circuit L1–
L2 (Figure 6-19), the loop equation is:
where
U,
I
are the (complex) measured values and
Z = R+ jX is the (complex) line impedance.
The line impedance is computed to be
Figure 6-19 Short circuit of a phase-phase loop
The calculation of the phase-phase loop does not take place as long as one of the con-
cerned phases is switched off (during single-pole dead time), to avoid an incorrect
measurement with the undefined measured values existing during this state. A state
I
L1
Z
L
I
L2
Z
L
U
L1–E
U
L2–E
–
=
⋅
–
⋅
Z
L
U
L1–E
U
L2–E
–
I
L1
I
L2
–
--------------------------------------
=
I
L1
I
L2
Z
L
Z
L
L1
L2
L3
E
U
L2–E
U
L1–E
Summary of Contents for siprotec 7SA522
Page 20: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 64: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 89: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Page 408: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 456: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 516: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 620: ...Appendix B 48 ...