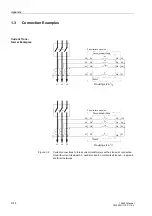
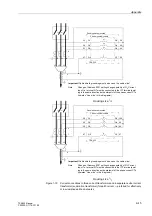
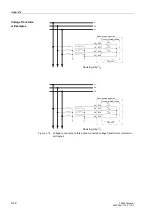
Appendix
A-7
7SA522 Manual
C53000-G1176-C119-2
7SA522
∗
−
∗
C /L
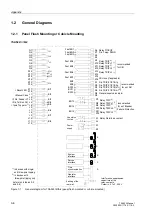
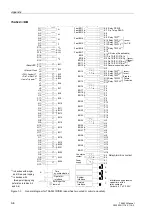
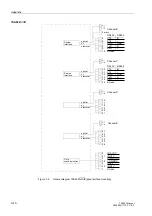
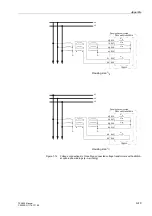
Figure 1-2
Connection diagram for 7SA522
∗
–
∗
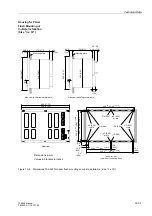
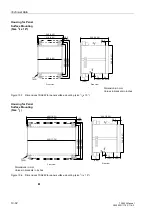
C/L (panel flush mounted or cubicle mounted)
Live status
Power
B
C
A
Earthing at the
supply
rear wall
Operator
interface
Q1
Q2
I
L1
Q7
Q8
I
4
Q3
Q4
I
L2
Q5
Q6
I
L3
R13
R14
U
4
R15
R17
U
L1
R16
K17
K18
BI1
U
L2
J3
J4
BI3
J5
J6
BI4
BI5
K3
K4
K1
K2
( )
~
+
-
R1
R2
BO8
R3
BO9
R5
BO10
K9
K10
Fast BO4
K11
K12
Fast BO5
contact
R18
U
L3
J1
J2
BI2
J7
J8
BI6
J9
J10
BI7
J11
J12
BI8
K6
K7
K8
Fast BO2
K5
Fast BO3
Fast BO1
K13
K14
Fast BO6
K15
K16
Fast BO7
R4
R6
BO12
BO11
R7
R8
BO13
R9
R10
BO14
R11
R12
BO15
D
E
P17
P18
BI9
N3
N4
BI11
N5
N6
BI12
BI13
N1
N2
BI10
N7
N8
BI14
N9
N10
BI15
N11
N12
BI16
P11
P12
BO21
P15
P16
BO23
P9
P10
BO20
P6
P7
P8
BO18
P5
BO19
BO17
P13
P14
BO22
3 2
1 2
BO16
P3
P4
3 2
1 2
Time
synchronization
Service
interface
System
interface
>Reset LED
>Manual Close
>FAIL: Feeder VT
>Dis.Tel.Rec.Ch1
>1poleTrip perm.
1)
Relay PICKUP
Dis. Telep. SEND
Relay TRIP
2)
Relay TRIP L1
1)
Relay TRIP L2
1)
Relay TRIP
2)
Relay TRIP L3
1)
recommended
for CB
Dis. TRIP Z1/Z1B, 1p
Dis. TRIP Z1/Z1B, 3p
Dis. TRIP Z1/Z1B, sf
2)
Dis. TRIP Z1/Z1B, mf
2)
General supervision alarm
Relay TRIP
2)
Relay TRIP L1
1)
Relay TRIP L2
1)
Relay TRIP
2)
Relay TRIP L3
1)
recommended
for ext.
Failure
recom.
for ext.
1)
in devices with single-
2)
in devices with
(refer also to tables 5-5
and three-pole tripping
three-pole tripping only
and 5-6)
AR
Breaker
Protection
Relay Alarm/Live contact
Interference suppression
capacitors at the
Ceramic, 4.7 nF, 250 V
relay contacts,
AR close (if applicable)
3 2
1 2
Summary of Contents for siprotec 7SA522
Page 20: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 64: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 89: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Page 408: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 456: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 516: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 620: ...Appendix B 48 ...