Section 19: Relay and Control Port Operation
T
ieline
T E C H N O L O G Y
Page 156
these cases a local power supply should be connected to the CAN 8+8. This
should be 9 volts DC, 500mA.
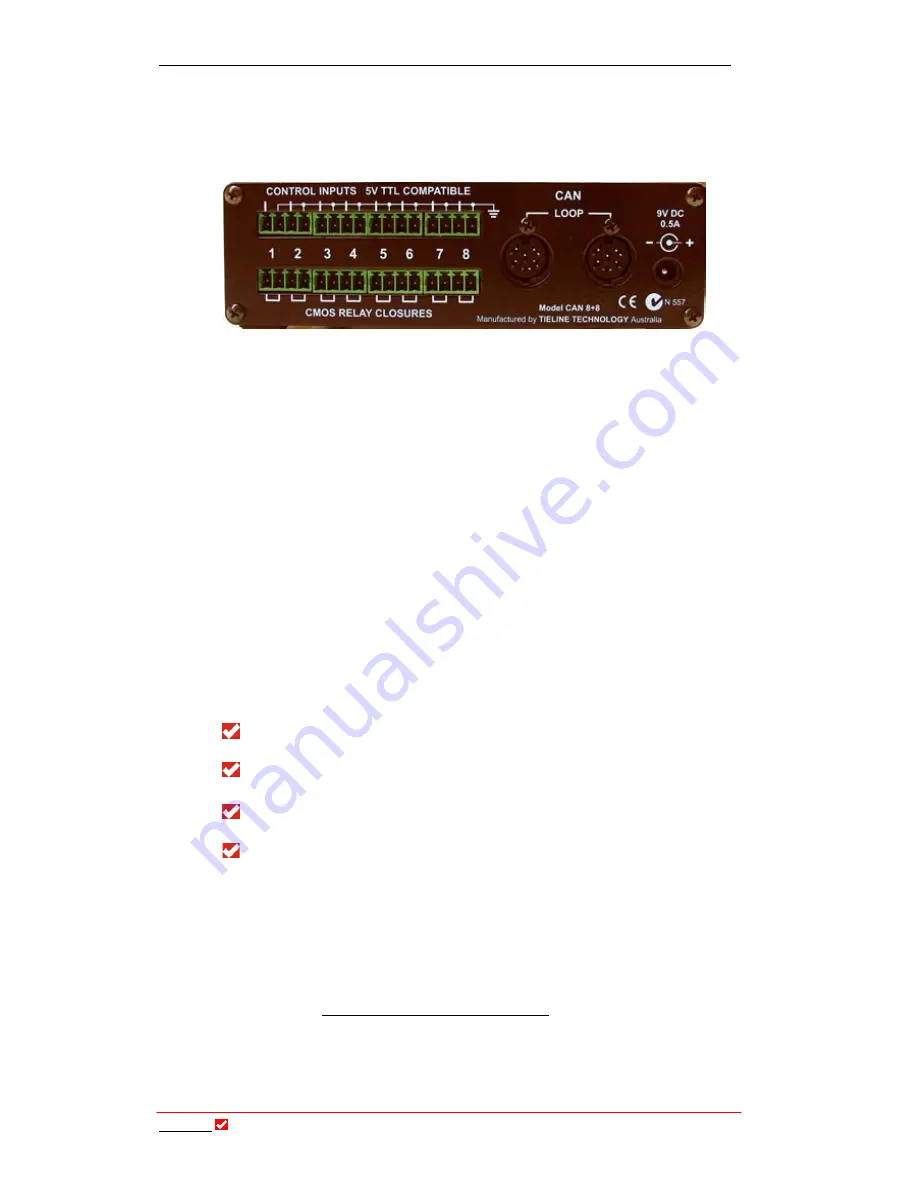
An external relay box is connected via the
CAN
port on the rear of the codec.
Figure 39: The Rear View of a CAN 8+8 External Relay Box
19.2.
Cabling and Operation Distances
A number of factors determine the maximum length. Firstly, there is the CAN
spec itself. This specifies a maximum length of 130m @ 500Kbps (the rate
T
ieline
codecs use). The second factor, which is often the limiting one, is the voltage
drop in the cable. Cable types, thickness, quality and length will all determine any
limitations in a unit’s performance.
Shielded dual twisted pair cables are recommended. Where cable runs are long
and master power source is being used, heavier conductors will be required.
Screw terminal plugs are provided to allow for easy on site wiring. These can be
hot plugged without any impact upon a unit’s performance.
In general,
T
ieline
recommends that the relay box should operate effectively on a
cable of 0.5 meters up to a maximum length of 75 meters from the codec.
Distances greater than this could be achievable. Following is a formula for
calculating maximum cable length:
V in(min) at relay box = 8V (minimum input voltage);
I (peak) at relay box = 250mA (peak current);
V out(min) at TLM600 (
i
-
Mix
G
3
) = 11V;
Max DC resistance (DCR) of cable = (11-8)/0.25 = 12 ohms.
Typically, 24AWG CAT5 cable has a DCR of about 0.095 ohms/meter.
Therefore, maximum length = (12/0.095)/2; dividing by 2 accounts for the
return path as well. In this example, the maximum theoretical length using this
cable’s specifications is about 63m.
A CAN cable wiring diagram is available in Appendix 1 of this reference manual.
This section is titled CAN Cable Wiring Configuration.
















































