Preliminary
www.ti.com
Architecture
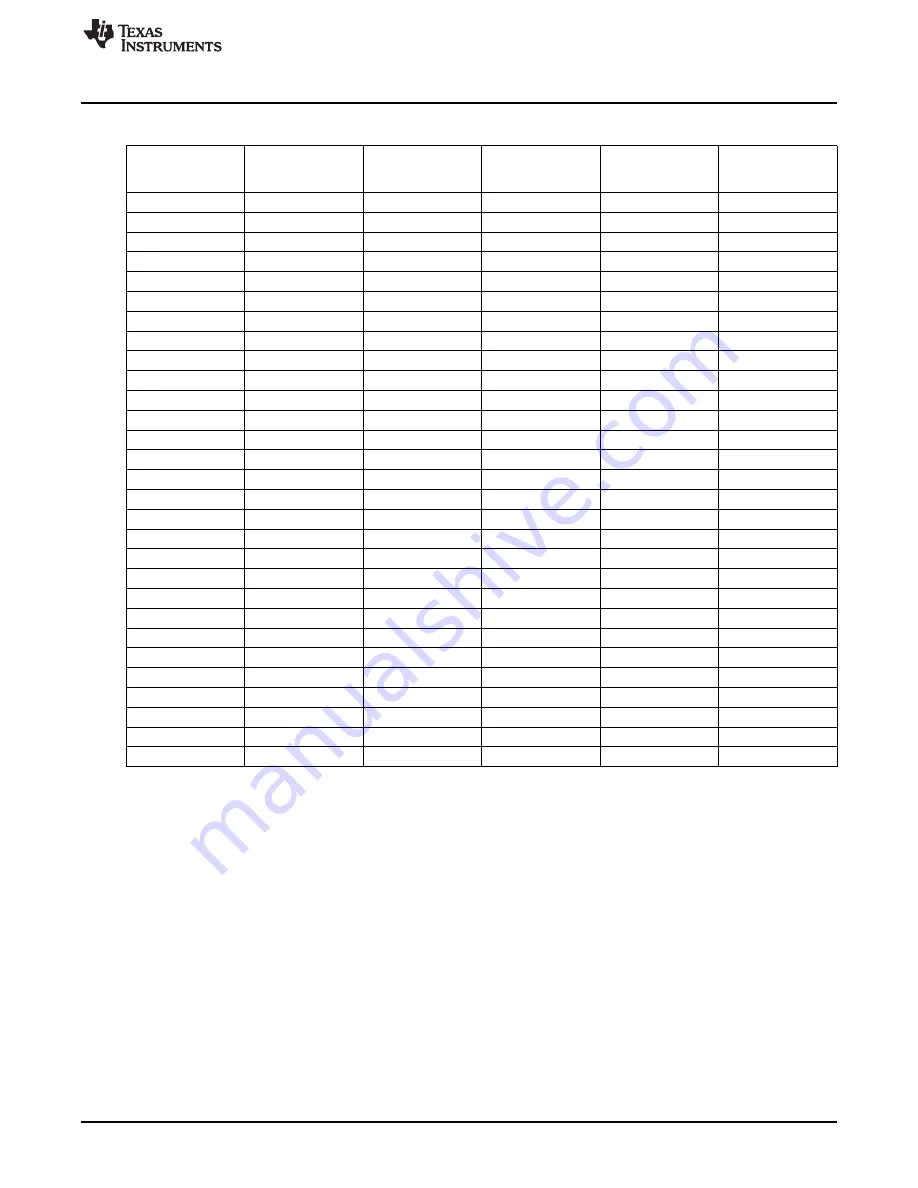
Table 5-2. GPMC Pin Multiplexing Options (continued)
Non Multiplexed
Non Multiplexed
Multiplexed
16-Bit NAND
GPMC Pin
Address Data
Address Data 8-Bit
Address Data
8-Bit NAND Device
Device
16-Bit Device
Device
16-Bit Device
GPMC_A[12]
A11
A12
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[11]
A10
A11
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[10]
A9
A10
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[9]
A8
A9
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[8]
A7
A8
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[7]
A6
A7
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[6]
A5
A6
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[5]
A4
A5
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[4]
A3
A4
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[3]
A2
A3
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[2]
A1
A2
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[1]
A0
A1
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_A[0]
Not Used
A0
Not Used
Not Used
Not Used
GPMC_D[15]
D15
Not Used
A16/D15
D15
Not Used
GPMC_D[14]
D14
Not Used
A15/D14
D14
Not Used
GPMC_D[13]
D13
Not Used
A14/D13
D13
Not Used
GPMC_D[12]
D12
Not Used
A13/D12
D12
Not Used
GPMC_D[11]
D11
Not Used
A12/D11
D11
Not Used
GPMC_D[10]
D10
Not Used
A11/D10
D10
Not Used
GPMC_D[9]
D9
Not Used
A10/D9
D9
Not Used
GPMC_D[8]
D8
Not Used
A9/D8
D8
Not Used
GPMC_D[7]
D7
D7
A8/D7
D7
D7
GPMC_D[6]
D6
D6
A7/D6
D6
D6
GPMC_D[5]
D5
D5
A6/D5
D5
D5
GPMC_D[4]
D4
D4
A5/D4
D4
D4
GPMC_D[3]
D3
D3
A4/D3
D3
D3
GPMC_D[2]
D2
D2
A3/D2
D2
D2
GPMC_D[1]
D1
D1
A2/D1
D1
D1
GPMC_D[0]
D0
D0
A1/D0
D0
D0
With all device types, the GPMC does not drive unnecessary address lines. They stay at their reset
value of 00.
Address mapping supports address/data-multiplexed 16-bit wide devices:
•
The NOR flash memory controller still supports non-multiplexed address and data memory devices.
•
Multiplexing mode can be selected through the GPMC_CONFIG1_i[9-8] MUXADDDATA bit field (i =
0 to 7).
•
Asynchronous page mode is not supported for multiplexed address and data devices.
555
SPRUGX9 – 15 April 2011
General-Purpose Memory Controller (GPMC)
© 2011, Texas Instruments Incorporated
















































