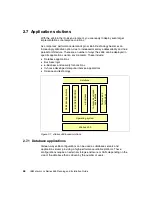
Chapter 2. Positioning
53
performance for complex computations that are required for data-mining,
scientific, and technical applications.
The Itanium 2 processor is the second in a family of Intel 64-bit enterprise-class
processors. For more information about the Intel Itanium 2 processor, see:
http://www.intel.com/products/server/processors/server/Itanium 2/
Intel Itanium Architecture-based microprocessors have the following features:
Advanced parallelism
High performance requires parallel execution, which is either very limited or
hardly achieved in today's architecture. The traditional PC systems are not
designed for parallelism, which is critical for current demanding applications
(for example, databases and application servers).
Today’s processors using limited parallelism are often 60 percent idle. When
source code is compiled on today’s systems, the result of the compilation is
sequential machine code. A regular (non-Itanium processor family) compiler
takes sequential code, examines and optimizes it for parallelism, but then has
to regenerate sequential code, but in such a way that the processor can
re-extract the parallelization from it. The processor will then be required to
read this implied parallelism from the machine code, re-build it, and execute it.
The parallelism is there, but it is not as obvious to the processor and more
work has to be done by the hardware before it can be utilized.
Itanium 2 supports parallelism on multiple levels. Instruction-level parallelism
(ILP) is the ability to execute multiple bundles (three instructions in a bundle)
at the same time. The Itanium 2 micro-architecture can deliver faster
performance by executing multiple bundles per clock cycle. Parallelism, both
at the instruction level and at the SMP system level, permits more efficient
use of virtually all system resources to enable improved scalability.
The Itanium processor's instruction-level parallelism helps ensure the
scalability necessary to manage large data warehouses.
Large memory addressability
Another key advantage is that 64-bit operating systems can support far more
physical memory than a 32-bit operating system. The limit for directly
addressable memory on 32-bit architecture is 4 GB. On 64-bit architecture is
it 16 Exabytes (EB) or 2
64
. The genuinely takes the processor to a level
where other hardware and software will take years to match its raw ability to
address and handle data.
Note: Performance should no longer be measured by just the speed in
MHz, but also by the degree of parallelism that the processor achieves.
Summary of Contents for 88553RX
Page 2: ......
Page 214: ...200 IBM Eserver xSeries 455 Planning and Installation Guide Figure 5 14 Connect to the x455...
Page 228: ...214 IBM Eserver xSeries 455 Planning and Installation Guide...
Page 229: ...IBM Eserver xSeries 455 Planning and Installation Guide...
Page 230: ......
Page 231: ......