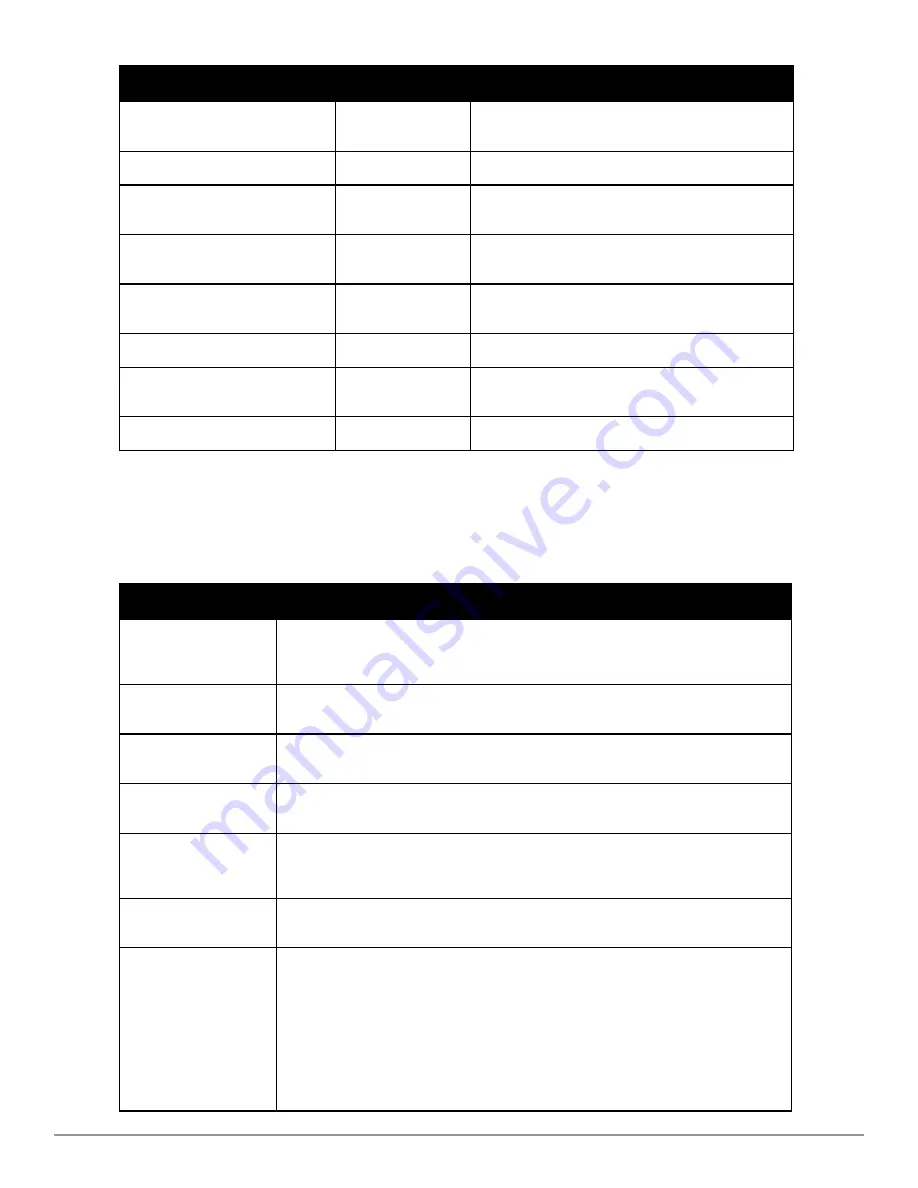
Key
Effect
Description
Ctrl F or the
right arrow
Forward
Move the cursor one character right.
Ctrl K
Delete Right
Delete all characters to the right of the cursor.
Ctrl N or the
down arrow
Next
Display the next command in the command history.
Ctrl P or
up arrow
Previous
Display the previous command in the command history.
Ctrl T
Transpose
Swap the character to the left of the cursor with the
character to the right of the cursor.
Ctrl U
Clear
Clear the line.
Ctrl W
Delete Word
Delete the characters from the cursor up to and
including the first space encountered.
Ctrl X
Delete Left
Delete all characters to the left of the cursor.
Specifying Addresses and Identifiers in Commands
This section describes addresses and other identifiers that you can reference in CLI commands.
Address/Identifier
Description
IP address
For any command that requires entry of an IP address to specify a network entity, use IPv4
network address format in the conventional dotted decimal notation (for example,
10.4.1.258).
Netmask address
For subnet addresses, specify a netmask in dotted decimal notation (for example,
255.255.255.0).
Media Access Control
(MAC) address
For any command that requires entry of a device’s hardware address, use the hexadecimal
format (for example, 00:05:4e:50:14:aa).
Service Set Identifier
(SSID)
A unique character string (sometimes referred to as a network name), consisting of no
more than 32 characters. The SSID is case-sensitive (for example, WLAN-01).
Basic Service Set
Identifier (BSSID)
This entry is the unique hard-wireless MAC address of the AP. A unique BSSID applies to
each frequency— 802.11a and 802.11g—used from the AP. Use the same format as for a
MAC address.
Extended Service Set
Identifier (ESSID)
Typically the unique logical name of a wireless network. If the ESSID includes spaces, you
must enclose the name in quotation marks.
Fast Ethernet or Gigabit
Ethernet interface
Any command that references a Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet interface requires that
you specify the corresponding port on the controller in the format <slot>/<port>:
<slot> is always 1, except when referring to interfaces on the W-6000M3 controller(slots 0-
3).
The <port> parameter refers to the network interfaces that are embedded in the front panel
of the W-3000 series controller, or a W-6000M3 controller module installed in a W-6000
controller chassis. Port numbers start at 0 from the left-most position.
Use the show port status command to obtain the interface information currently available
from a controller.
Table 4:
Addresses and Identifiers
Dell PowerConnect W-Series ArubaOS 6.2 |
Reference Guide
Introduction | 13
Summary of Contents for PowerConnect W-7200 Series
Page 1: ...Dell PowerConnect W Series ArubaOS 6 2 Command Line Interface Reference Guide ...
Page 38: ...38 aaa authentication server windows DellPowerConnect W Series ArubaOS 6 2 Reference Guide ...
Page 319: ...DellPowerConnect W Series ArubaOS 6 2 Reference Guide interface loopback 319 ...
Page 346: ...346 ipv6 mld DellPowerConnect W Series ArubaOS 6 2 Reference Guide ...
Page 387: ...DellPowerConnect W Series ArubaOS 6 2 Reference Guide ip radius 387 ...
Page 995: ...DellPowerConnect W Series ArubaOS 6 2 Reference Guide show firewall 995 ...
Page 1529: ...DellPowerConnect W Series ArubaOS 6 2 Reference Guide wms client 1529 ...
Page 1536: ...0510956 01 March 2013 1536 ...














































