Functional Description
209
SLAU723A – October 2017 – Revised October 2018
Copyright © 2017–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
System Control
3. An internal system reset is initiated.
4. Reset is deasserted and the processor is directed to the NMI handler during the reset sequence.
4.1.5.5
PLL
The PLL has two modes of operation: normal and power-down. The modes are programmed using the
PLLPWR bit in the PLLFREQ0 register (see
).
•
Normal: The PLL oscillates based on the values in the PLLFREQ0 and PLLFREQ1 registers and
drives the output.
•
Power-down: Most of the PLL internal circuitry is disabled and the PLL does not drive the output.
4.1.5.5.1 PLL Configuration
The PLL is disabled by default during power-on reset and is enabled later by software if required. Software
specifies the output divisor to set the system clock frequency and enables the PLL to drive the output. The
PLL is controlled using the PLLFREQ0, PLLFREQ1, and PLLSTAT registers. Changes made to these
registers do not become active until after the NEWFREQ bit in the RSCLKCFG register is enabled. The
clock source for the main PLL is selected by configuring the PLLSRC field in the Run and Sleep Clock
Configuration (RSCLKCFG) register. The PLL allows for the generation of system clock frequencies in
excess of the reference clock provided. The reference clocks for the PLL are the PIOSC and the MOSC.
The PLL is controlled by two registers, PLLFREQ0 and PLLFREQ1. The PLL VCO frequency (f
VCO
) is
determined through
f
VCO
= f
IN
× MDIV
where
•
f
IN
= f
XTAL
/ (Q+1)(N+1) or f
PIOSC
/ (Q+1)(N+1)
•
MDIV = MINT + (MFRAC / 1024)
(1)
The Q and N values are programmed in the PLLFREQ1 register. To reduce jitter, program MFRAC to 0x0.
When the PLL is active, the system clock frequency (SysClk) is calculated using
SysClk = f
VCO
/ (1 + 1)
(2)
The PLL system divisor factor (PSYSDIV) must be set as 1.
lists examples of the system clock
frequency.
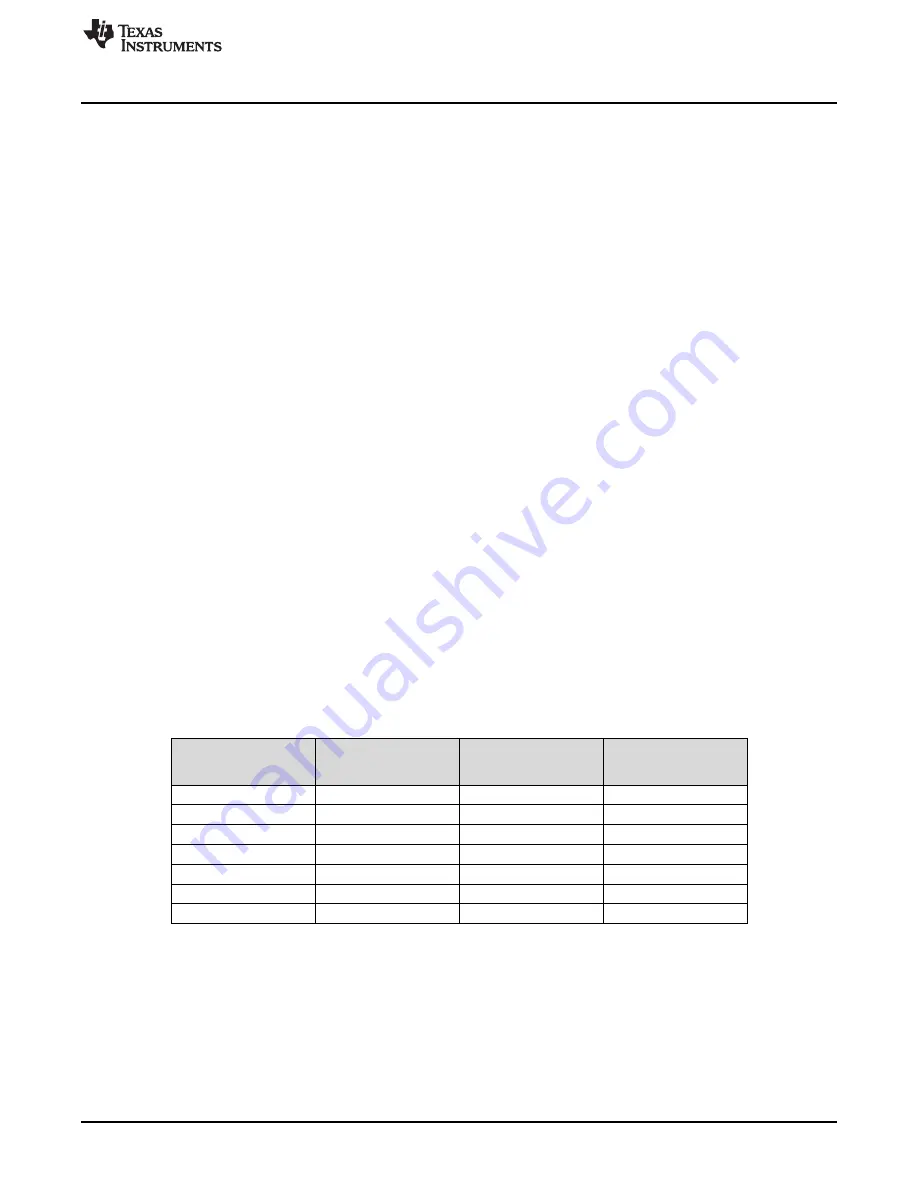
Table 4-5. Examples of System Clock Frequencies
f
VCO
(MHz)
Q
P 1
System Clock
(SYSCLK) Frequency
(MHz)
480
2
2
120
480
3
2
80
480
4
2
60
480
5
2
48
320
2
2
80
320
3
2
53
320
4
2
40
If the MOSC provides the clock reference to the PLL, the translation provided by hardware and used to
program the PLL is available for software in the PLL Frequency n (PLLFREQn) registers (see
). The internal translation provides a translation within ±1% of the targeted PLL VCO
frequency.
shows the actual PLL frequency and error for a given crystal choice.
provides examples of the programming expected for the PLLFREQ0 and PLLFREQ1 registers.
The Crystal Frequency column specifies the input crystal frequency, and the PLL Frequency column lists
the PLL frequency given the values of MINT and N, when Q = 0.






























