Step 2: Performing a zero point adjustment
The second step in the troubleshooting procedure is to zero point adjust the device. For further
information on zero point adjustment, see Commissioning (Page 91).
Step 3: Calculating the measurement error
The result of the zero point adjustment will show you if the zero point was set under good and
stable conditions.
The lower the obtained value of the parameter Zero Point Standard Deviation, the lower is the
achievable measuring error. For a well-installed flowmeter, the Zero Point Standard Deviation
corresponds to the specified zero point stability for the sensor size, see Performance
(Page 215).
The parameter Zero Point Standard Deviation is located in the Maintenance & Diagnostics
menu in the SIMATIC PDM.
Calculating the measurement error
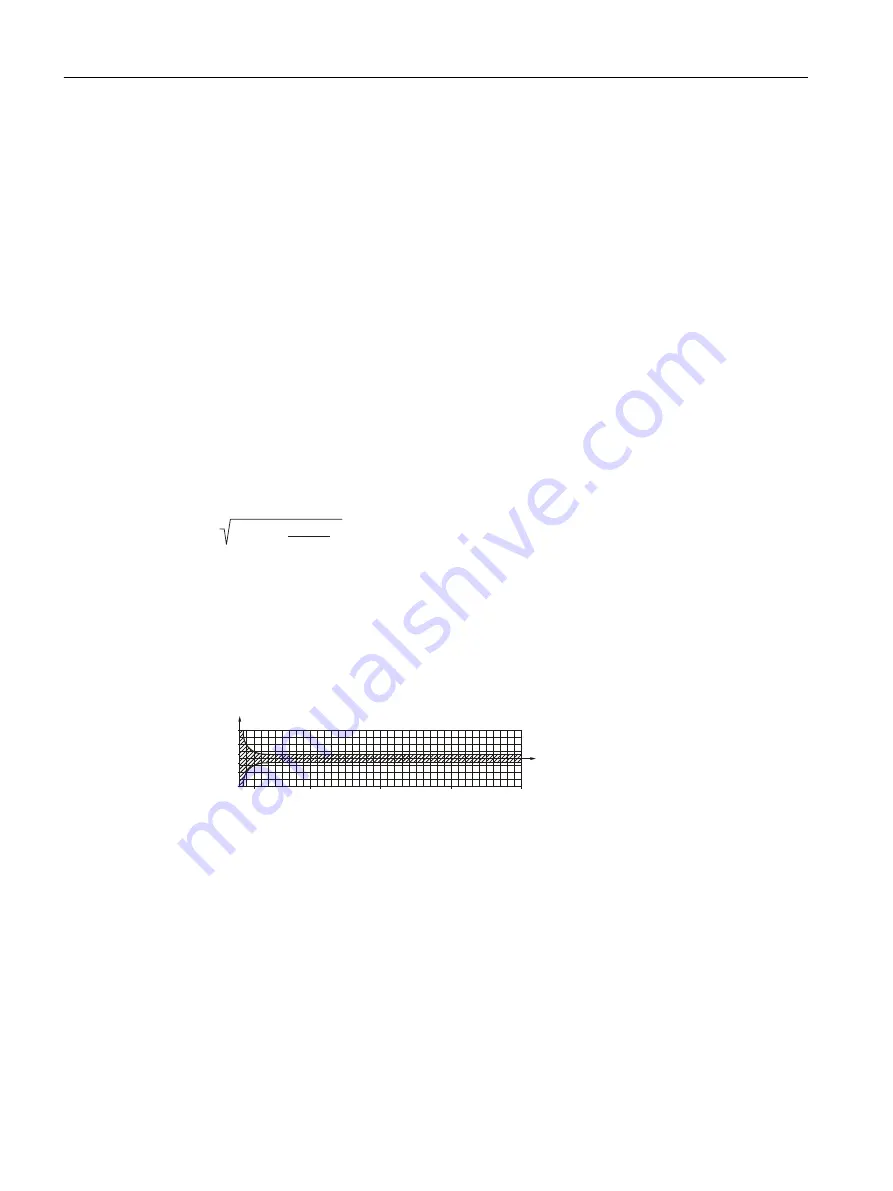
● The error curve is plotted from the formula:
E = ± (Cal)
2
+
z x 100
qm
( )
2
E
= Error [%]
Z
= Zero point [kg/h]
qm = Mass flow [kg/h]
Cal. = Calibrated flow accuracy: 0.10 or 0.15
FSO (sensors
max. flow rate)
Error in % of actual mass flow rate with 95% confidence
(probability)
Actual mass
flow rate
-1.0
-0.5
1.0
0.5
0.15
-0.15
50%
25%
5%
75%
100%
Table 10-2
Reference conditions for flow calibrations (ISO 9104 and DIN/EN 29104)
Flow conditions Fully developed flow profile
Temperature,
medium
20 °C ± 2 °C (68 °F ± 3.6 °F)
Temperature,
ambient
20 °C ± 2 °C (68 °F ± 3.6 °F)
Liquid pressure 2 ± 1 bar
Density
0.997 g/cm3
Brix
40 °Brix
Diagnosing and troubleshooting
10.3 Operation troubleshooting
MASS 2100 & FC300 (FCT030)
210
Operating Instructions, 06/2017, A5E39789040-AA






























