-
99
-
Read
the
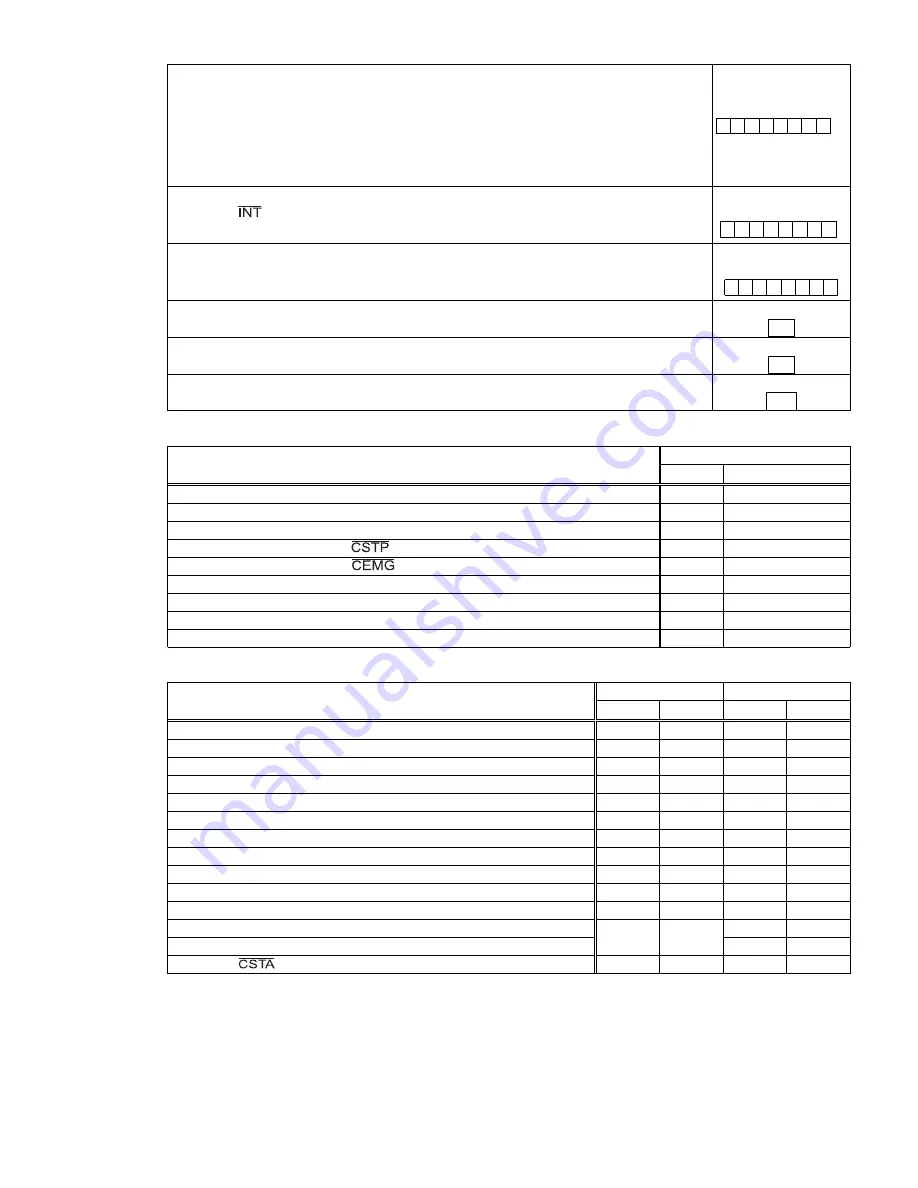
interrupt
status
<SENI(bit2),
SERR
(bit
4),
SINT
(bit
5)
in
MSTSW>
SENI
=
1:
When
IEND
=
1
and
a
stop
interrupt
occurs,
make
this
bit
1.
After
reading
MSTS,
it
will
become
0.
SERR
=
1:
Becomes
1
when
an
error
interrupt
occurs.
Becomes
0
by
reading
REST.
SINT
=
1:
Becomes
1
when
an
event
interrupt
occurs.
Becomes
0
by
reading
RIST.
[MSTSW]
(READ)
7
0
-
-
n
n
-
n
-
-
Set
the
interrupt
mask
<INTM
(bit
29)
in
RENV1>
1:
Mask
output.
[RENV1]
(WRITE)
31
24
-
-
n
-
-
-
-
-
Setting
a
stop
interrupt
<IEDN
(bit
30)
in
RENV2>
1:
Enable
a
stop
interrupt.
[RENV2]
(WRITE)
31
24
0
n
-
-
-
-
-
-
Read
the
cause
of
the
error
interrupt
<RREST:
Read
out
command>
Copy
the
data
in
the
REST
register
(error
interrupt
cause)
to
BUF.
[Read
command]
F2h
Read
the
event
interrupt
cause
<RRIST:
Read
out
command>
Copy
the
data
in
the
RIST
register
(event
interrupt
cause)
to
BUF.
[Read
command]
F3h
Set
the
event
interrupt
cause
<WRIRQ:
Write
command>
Write
the
BUF
data
to
the
RIRQ
register
(event
interrupt
cause).
[Write
command]
ACh
[Error
interrupt
causes]
<Detail
of
REST:
The
cause
of
an
interrupt
makes
the
corresponding
bit
"1">
Cause
(REST)
Error
interrupt
cause
Bit
Bit
name
Stopped
by
turning
ON
the
+EL
input
0
ESPL
Stopped
by
turning
ON
the
-EL
input
1
ESML
Stopped
by
turning
ON
the
ALM
input
2
ESAL
Stopped
by
turning
ON
the
input
3
ESSP
Stopped
by
turning
ON
the
input
4
ESEM
Deceleration
stopped
by
turning
ON
the
SD
input
5
ESSD
Stopped
by
an
overflow
of
PA/PB
input
buffer
counter
occurrence
6
ESPO
An
EA/EB
input
error
occurred
(does
not
stop).
7
ESEE
A
PA/PB
input
error
occurred
(does
not
stop).
8
ESPE
[Event
interrupt
causes]
<
The
corresponding
interrupt
bit
is
set
to
1
and
then
an
interrupt
occurred>
Set
cause
(RIRQ)
Cause
(RIST)
Event
interrupt
cause
Bit
Bit
name
Bit
Bit
name
Automatic
stop
0
IREN
0
ISEN
When
enabled
to
write
to
the
pre-register.
1
IRNM
1
ISNM
When
acceleration
starts
2
IRUS
2
ISUS
When
acceleration
ends
3
IRUE
3
ISUE
When
deceleration
starts
4
IRDS
4
ISDS
When
deceleration
ends
5
IRDE
5
ISDE
When
the
Comparator
1
conditions
are
satisfied
6
IRC1
6
ISC1
When
the
Comparator
2
conditions
are
satisfied
7
IRC2
7
ISC2
When
the
counter
value
is
latched
by
an
LTC
input
8
IRLT
8
ISLT
When
the
counter
value
is
latched
by
an
ORG
input
9
IROL
9
ISOL
When
the
SD
input
is
turned
ON
10
IRSD
10
ISSD
When
the
+DR
input
changes
11
ISPD
When
the
-DR
input
changes
11
IRDR
12
ISMD
When
the
input
is
turned
ON
12
IRSA
13
ISSA
Summary of Contents for PCL6113
Page 1: ...User s Manual For PCL6113 6123 6143 Pulse Control LSI Nippon Pulse Motor Co Ltd...
Page 11: ...5 3 Terminal Assignment Diagram 3 1 PCL6113 3 2 PCL6123...
Page 20: ...14 5 Block Diagram...
Page 115: ...109 11 Stop timing by error...
Page 116: ...110 13 External Dimensions 13 1 PCL6113...
Page 117: ...111 13 2 PCL6123...
Page 118: ...112 13 3 PCL6143...
















































