-
48
-
9.
Operation
Mode
Specify
the
basic
operation
mode
using
the
MOD
area
(bits
0
to
6)
in
the
RMD
(operation
mode)
register.
9-1.
Continuous
operation
mode
using
command
control
This
is
a
mode
of
continuous
operation.
A
start
command
is
written
and
operation
continues
until
a
stop
command
is
written.
MOD
Operation
method
Direction
of
movement
00h
Continuous
operation
from
a
command
Positive
direction
08h
Continuous
operation
from
a
command
Negative
direction
Stop
by
turning
ON
the
EL
signal
corresponding
to
the
direction
of
operation.
When
operation
direction
is
positive,
+EL
can
be
used.
When
operation
direction
is
negative,
-EL
is
used.
In
order
to
start
operation
in
the
reverse
direction
after
stopping
the
motion
by
turning
ON
the
EL
signal,
a
new
start
command
must
be
written.
9-2.
Positioning
operation
mode
The
following
2
operation
types
are
available
for
positioning
operations.
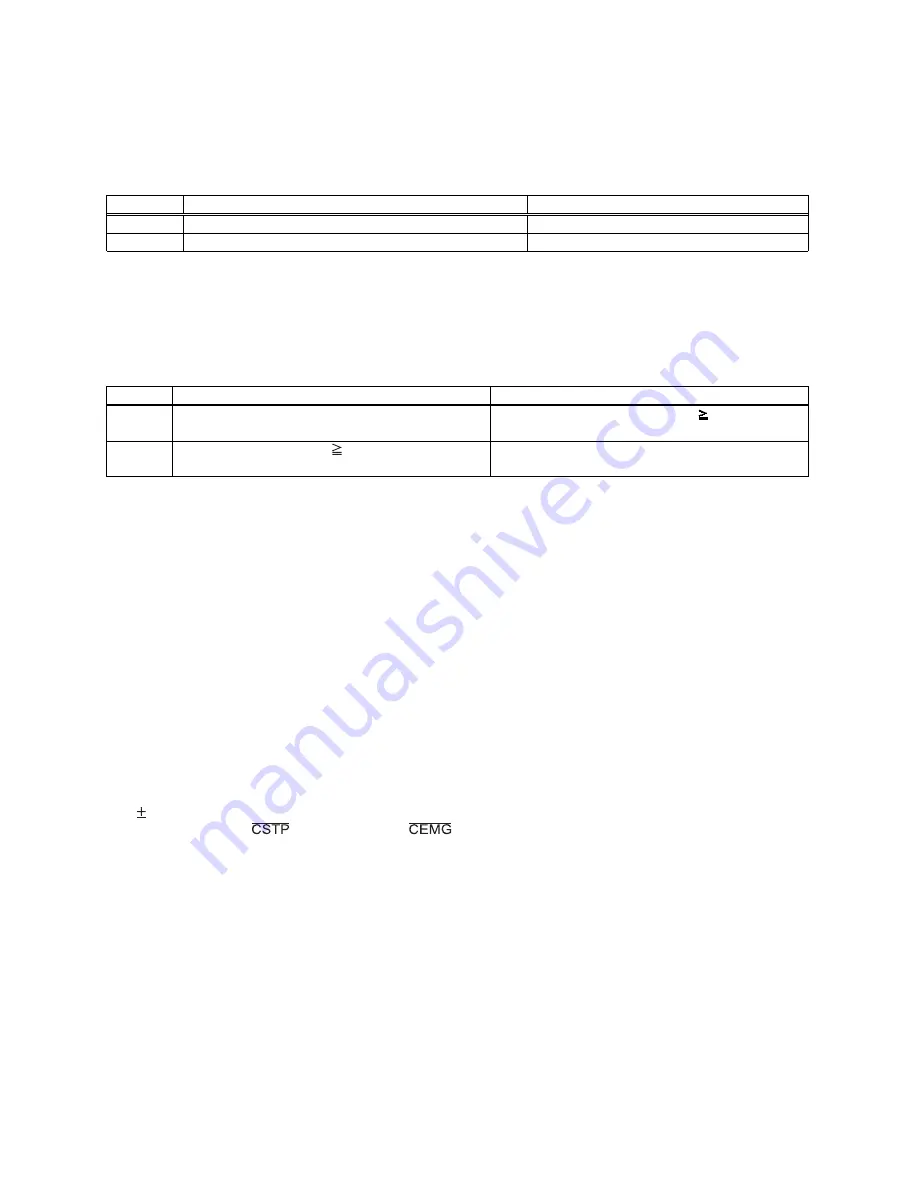
MOD
Operation
method
Direction
of
movement
41h
Positioning
operation
Positive
direction
when
PRMV
0
Negative
direction
when
PRMV
<
0
47h
Timer
operation
(PRMV 0)
Positive
direction
(DIR
=
H).
However,
the
pulse
output
is
masked.
9-2-1.
Positioning
operation
(MOD:
41h)
This
is
a
positioning
mode
used
by
placing
a
value
in
the
PRMV
(target
position)
register.
The
feed
direction
is
determined
by
the
sign
set
in
the
PRMV
register.
When
starting,
the
RMV
register
absolute
setting
value
is
loaded
into
the
positioning
counter
(RPLS).
The
PCL
counts
down
pulses
with
operations,
and
when
the
value
of
the
positioning
counter
drops
to
0,
movement
on
the
axes
stops.
When
you
set
the
PRMV
register
value
to
zero
to
start
a
positioning
operation,
the
LSI
will
stop
outputting
pulses
immediately.
9-2-2.
Timer
operation
(MOD:
47h)
This
mode
allows
the
internal
operation
time
to
be
used
as
a
timer.
The
internal
effect
of
this
operation
is
identical
to
the
positioning
operation.
However,
the
LSI
does
not
output
any
pulses
(they
are
masked).
Therefore,
the
internal
operation
time
using
the
low
speed
start
command
will
be
a
product
of
the
frequency
of
the
output
pulses
and
the
RMV
register
setting.
(Ex.:
When
the
frequency
is
1000
pps
and
the
RMS
register
is
set
to
120
pulses,
the
internal
operation
time
will
be
120
msec.)
Write
a
positive
number
(1
to
134,217,727)
into
the
RMV
register.
Negative
numbers
are
treated
as
unsigned
positive
numbers.
The
EL
input
signal,
SD
input
signal,
and
ALM
input
are
ignored.
(These
are
always
treated
as
OFF.)
The
ALM
input
signal
input
signal,
and
input
signals
are
effective.
The
direction
change
timer
function
is
disabled.
Regardless
of
the
MINP
setting
(bit
9)
in
the
RMD
(operation
mode)
register,
an
operation
complete
delay
controlled
by
the
INP
signal
will
not
occur.
In
order
to
eliminate
deviations
in
the
internal
operation
time,
set
the
METM
(bit
12)
in
the
PRMD
register
to
zero
and
use
the
cycle
completion
timing
of
the
output
pulse
as
the
operation
complete
timing.
Summary of Contents for PCL6113
Page 1: ...User s Manual For PCL6113 6123 6143 Pulse Control LSI Nippon Pulse Motor Co Ltd...
Page 11: ...5 3 Terminal Assignment Diagram 3 1 PCL6113 3 2 PCL6123...
Page 20: ...14 5 Block Diagram...
Page 115: ...109 11 Stop timing by error...
Page 116: ...110 13 External Dimensions 13 1 PCL6113...
Page 117: ...111 13 2 PCL6123...
Page 118: ...112 13 3 PCL6143...
















































