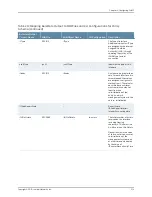
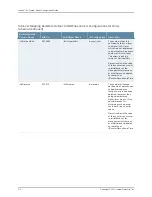
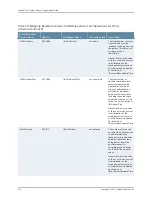
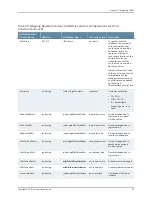
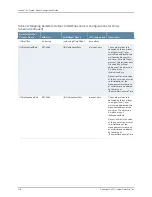
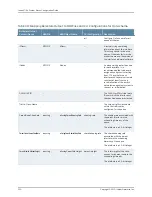
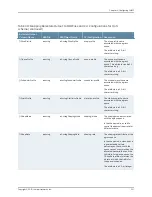
The % variables in the remote name are replaced at runtime with the sysName and
sysUpTime parameters to produce variable filenames on the remote host.
See the bulkstats receiver remote-name command.
host1(config)#
bulkstats receiver 1 remote-name “ bulk%s%d.sts” sysName
collectorSequence
Guidelines
The current capabilities and limitations of the bulk statistics formatter are:
•
If you add %d or any numeric formatter for a string value (such as sysName), the
attribute name will be used (for instance, sysName). The opposite is also true, except
for sysUptime, which will use %s as a %u.
•
You can use %% if you want a % character to be part of the parsed name.
•
You can use the same attribute multiple times. For example, you may want a name
that has %x and %u of collectorSequence.
•
Currently, there is no control over sequence numbers, except for the guarantee that
the formatter will:
1.
Use sequential values, beginning from 1
2.
Persist through system reboot
•
If you need the sequential number to restart, remove and then add the bulk statistics
receiver again.
•
You can use up to 128 characters for the remote file name. Anything beyond that is
truncated when the filename is stored in nonvolatile memory, but this truncation is not
visible until the next time the system reboots.
Specifying End of Line Format
By default, the bulk statistics application generates a DOS-compatible file that contains
both a carriage return (CR) and line feed (LF) at the end of each line. The existence of a
carriage return at the end of a line may cause formatting issues with some applications
that do not ignore or remove carriage returns.
You can set up the system to remove the carriage return and leave only a line feed at the
end of each line.
bulkstats file-format endOfLine-LF
•
Use to strip the carriage return from the end of each line in the bulkstats file.
•
Example
host1(config)#
bulkstats file-format endOfLine-LF
•
Use the
no
version to return to the default, CR and LF.
•
See bulkstats file-format endOfLine-LF.
227
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
Chapter 4: Configuring SNMP
Summary of Contents for JUNOSE 11.3
Page 6: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc vi...
Page 8: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc viii JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 24: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc xxiv JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 32: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 2 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 146: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 116 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 166: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 136 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 432: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 402 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 488: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 458 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 524: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 494 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 554: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 524 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 566: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 536 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 588: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 558 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 613: ...PART 3 Index Index on page 585 583 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc...
Page 614: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 584 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 632: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 602 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...