•
Specify neither the
primary-srp
nor the
standby-srp
keyword to stop operation on
both SRP modules.
•
Specify the keyword
primary-srp
to stop operation on the primary SRP module only.
This action causes the redundant SRP module to assume the primary role.
•
Specify the keyword
standby-srp
to stop operation on the redundant SRP module
only.
•
If you do not specify the
force
keyword, the procedure fails if:
•
The SRP modules are in certain states, such as during a synchronization. In these
cases, the router will display a message that indicates that the procedure cannot
currently be performed and the reason why. However, if the SRP modules are in
other states that could lead to a loss of configuration data or NVS corruption, the
router displays a message that explains the state of the SRP modules and asks
you to confirm (enter yes or no) whether you want to proceed.
•
The SRP modules are in any state that could lead to loss of configuration data or
NVS corruption, and the router will display a message that explains why the
command failed.
•
In Boot mode, you cannot issue any keywords with this command.
•
When the high availability state is active or pending, this command ensures that the
router configuration, up to when you issued the
halt
command, is mirrored to the
standby SRP.
•
When you issue this command, the router prompts you for a confirmation before the
procedure starts.
•
Remove or power down the SRP module within 2 minutes of executing the
halt
command. Otherwise, the SRP module will automatically reboot.
•
Examples
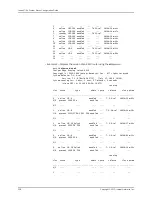
host1#
halt
host1#
halt primary-srp
host1#
halt standby-srp force
•
There is no
no
version.
•
See halt.
Replacing Line Modules on ERX Routers, the E120 Router, and the E320 Router
You can install line modules in slots previously occupied by different types of line modules.
For example, on the ERX1440 router, you can replace a GE-2 line module and a GE-2 SFP
I/O module in a slot that previously contained an OCx/STMx/DS3-ATM line module and
an OC3-4 I/O module.
When you configure a line module and an I/O module or IOAs, the router stores the
configuration in NVS. In some cases, you must erase the interface configuration on the
slot and reconfigure it after you have installed the new line module. However, some line
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
350
JunosE 11.3.x System Basics Configuration Guide
Summary of Contents for JUNOSE 11.3
Page 6: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc vi...
Page 8: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc viii JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 24: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc xxiv JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 32: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 2 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 146: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 116 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 166: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 136 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 432: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 402 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 488: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 458 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 524: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 494 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 554: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 524 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 566: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 536 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 588: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 558 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 613: ...PART 3 Index Index on page 585 583 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc...
Page 614: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 584 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 632: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 602 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...