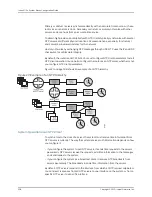
Primary
or
stratum 1
servers synchronize directly with an accurate time source, such as a
radio clock or an atomic clock.
Secondary
or
stratum n
servers synchronize with other
servers, and are
n
hops from an accurate time source.
To obtain high precision and reliability with NTP, clients typically synchronize with several
NTP servers at different physical locations. Peer associations, especially for stratum 1
and 2 servers, provide redundancy for the network.
Hosts synchronize by exchanging NTP messages through UDP. NTP uses the IP and UDP
checksums to confirm data integrity.
By default, the router is an NTP client. You must configure NTP client parameters to start
NTP client operation. You can also configure the router as an NTP server, whether or not
you configure NTP client parameters.
Figure 27 on page 508 shows an example of an NTP hierarchy.
Figure 27: Example of an NTP Hierarchy
System Operation as an NTP Client
To synchronize to the clock of a server, the system must receive time information from
NTP servers recurrently. The way the system receives such information depends on how
you configure it:
•
If you configure the system to poll NTP servers, it sends time requests to the servers
periodically. NTP servers receive the requests, add time information to the messages,
and send replies to the system.
•
If you configure the system as a broadcast client, it receives NTP broadcasts from
servers periodically. The broadcasts include time information from the servers.
By default, NTP servers respond to the interface from which an NTP request originated.
You can direct responses from all NTP servers to one interface on the system, or from a
specific NTP server to a specific interface.
Copyright © 2010, Juniper Networks, Inc.
508
JunosE 11.3.x System Basics Configuration Guide
Summary of Contents for JUNOSE 11.3
Page 6: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc vi...
Page 8: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc viii JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 24: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc xxiv JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 32: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 2 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 146: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 116 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 166: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 136 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 432: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 402 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 488: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 458 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 524: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 494 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 554: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 524 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 566: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 536 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 588: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 558 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 613: ...PART 3 Index Index on page 585 583 Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc...
Page 614: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 584 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...
Page 632: ...Copyright 2010 Juniper Networks Inc 602 JunosE 11 3 x System Basics Configuration Guide...